Intro
Discover 5 ways to find P value, a crucial statistic in hypothesis testing, using t-tests, ANOVA, and regression analysis, with steps to calculate probability values and interpret results accurately.
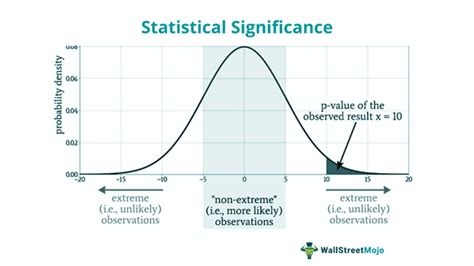
Understanding the concept of p-value is crucial in statistical analysis, as it helps researchers determine the significance of their findings. The p-value, or probability value, is a key component in hypothesis testing, indicating the probability of observing results at least as extreme as those observed, assuming that the null hypothesis is true. In this article, we will delve into the importance of p-values, their interpretation, and most importantly, how to find them using various methods.
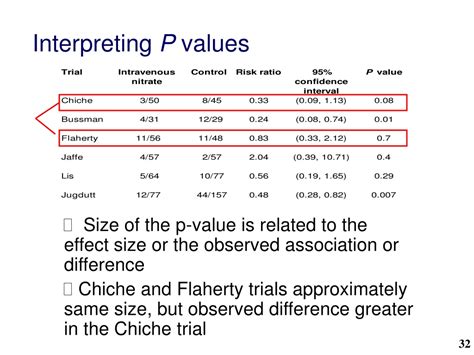
The p-value is a measure that helps researchers understand whether their data supports a claim or not. A small p-value indicates that the observed data would be very unlikely under the null hypothesis, leading to the rejection of the null hypothesis. On the other hand, a large p-value suggests that the data is consistent with the null hypothesis, and thus, the null hypothesis is not rejected. Given its critical role in statistical analysis, finding the p-value accurately is paramount.
There are several methods to calculate the p-value, depending on the type of data and the statistical test being performed. Here, we will explore five common ways to find the p-value, including using statistical software, p-value tables, online calculators, programming languages, and manual calculations for simple tests.
Understanding P-Value
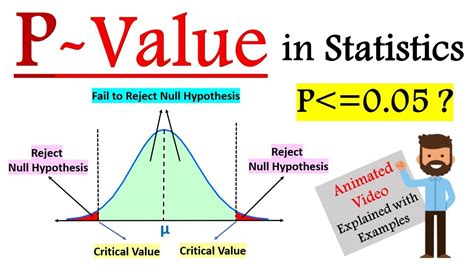
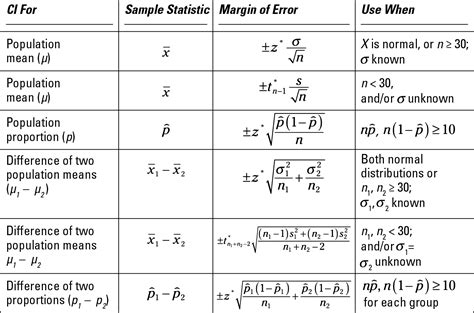
Before diving into the methods of finding p-values, it's essential to understand what a p-value represents. The p-value is a probability that ranges from 0 to 1, where a value close to 0 indicates strong evidence against the null hypothesis, and a value close to 1 indicates weak evidence against the null hypothesis. The choice of the significance level, often denoted as alpha (α), determines the threshold below which the null hypothesis is rejected. Commonly, α is set to 0.05, meaning that if the p-value is less than 0.05, the results are considered statistically significant.
Method 1: Using Statistical Software
Statistical software packages such as R, SPSS, SAS, and Python libraries (e.g., scipy, statsmodels) are powerful tools for calculating p-values. These programs can perform a wide range of statistical tests, from simple t-tests to complex regression analyses, and provide the p-value as part of the output. For example, in R, the t.test() function calculates the p-value for a t-test, while in Python, the scipy.stats.ttest_ind() function serves a similar purpose. The use of statistical software is highly recommended due to its accuracy and efficiency.
Steps for Using Statistical Software
- Choose the appropriate statistical test based on your research question and data type. - Input your data into the software. - Select the correct options for the test, including the type of test and any relevant parameters. - Run the test and obtain the p-value from the results.Method 2: P-Value Tables
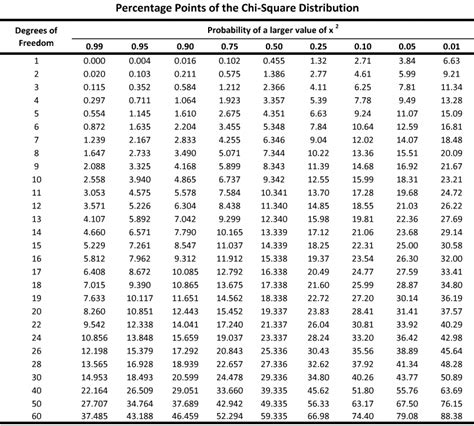
For simpler tests, such as z-tests or t-tests, p-value tables can be used. These tables list the critical values for different significance levels, allowing researchers to look up the p-value corresponding to their test statistic. While less versatile than statistical software, p-value tables are useful for quick references or when working without access to a computer.
Using P-Value Tables
- Determine the test statistic from your data. - Choose the correct table based on the type of test (z-test, t-test, etc.). - Look up the test statistic in the table to find the corresponding p-value.Method 3: Online Calculators
There are numerous online calculators available that can calculate p-values for various statistical tests. These calculators are web-based tools that require input of the test statistic and other relevant parameters, then provide the p-value. They are convenient for quick calculations and can be accessed from any device with an internet connection.
Steps for Using Online Calculators
- Find a reliable online calculator for the specific statistical test. - Input the required data, such as the test statistic and sample size. - Calculate the p-value using the online tool.Method 4: Programming Languages

Programming languages like Python, R, and MATLAB offer extensive libraries and functions for statistical analysis, including p-value calculations. These languages are particularly useful for complex analyses, large datasets, and automation of repetitive tasks. Scripts can be written to perform specific statistical tests and calculate p-values, providing a flexible and powerful approach to data analysis.
Calculating P-Value with Programming Languages
- Choose a programming language suitable for your analysis. - Import the necessary libraries or modules for statistical functions. - Write a script to perform the desired statistical test and calculate the p-value.Method 5: Manual Calculation

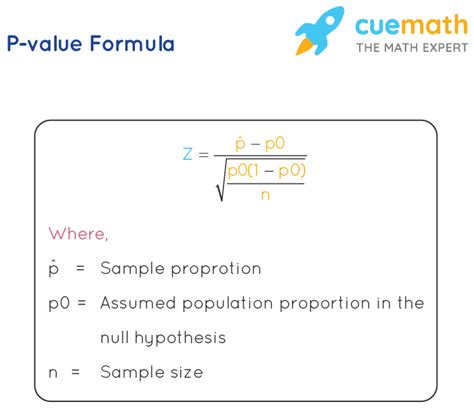
For simple statistical tests, it's possible to manually calculate the p-value using statistical formulas. This method is more time-consuming and prone to errors compared to using software or online tools but can be useful for educational purposes or when understanding the underlying mathematics is essential.
Manual P-Value Calculation Steps
- Identify the appropriate statistical formula for the test. - Calculate the test statistic using your data. - Apply the formula to find the p-value, which may involve integrating a probability distribution function.P-Value Calculation Methods Gallery



What is the purpose of calculating the p-value in statistical analysis?
+The p-value helps determine the significance of the results, indicating whether the observed effects are due to chance or if they reflect a real phenomenon.
How do I choose the correct method for calculating the p-value?
+The choice of method depends on the type of data, the statistical test being performed, and personal preference. Statistical software and online calculators are often the most convenient and accurate methods.
What is the difference between a p-value and statistical significance?
+Statistical significance is determined by whether the p-value is below a certain threshold (usually 0.05), indicating that the results are unlikely to occur by chance. The p-value itself quantifies the evidence against the null hypothesis.
In conclusion, calculating the p-value is a critical step in statistical analysis, providing insight into the significance of research findings. By understanding the different methods available for calculating p-values, researchers can choose the approach that best suits their needs, ensuring accurate and reliable results. Whether using statistical software, online calculators, programming languages, or manual calculations, the key is to select a method that aligns with the research question and data characteristics, ultimately contributing to the advancement of knowledge in various fields. We invite readers to share their experiences with p-value calculations and the challenges they have faced in interpreting statistical significance in their research endeavors.