Physical Therapy For Meniscus Tear
Meniscus tears are a common injury affecting the knee joint, causing pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. The meniscus, a cartilage structure in the knee, plays a crucial role in absorbing shock, stabilizing the joint, and facilitating smooth movement. When a meniscus tear occurs, physical therapy emerges as a vital component of the rehabilitation process, helping individuals regain strength, flexibility, and function.
Understanding Meniscus Tears
Before delving into the role of physical therapy, it’s essential to understand the nature of meniscus tears. The meniscus can tear due to a sudden injury, often occurring during sports activities, or as a result of wear and tear over time. Tears can be classified based on their location, size, and shape, with some tears being more amenable to conservative management than others. Symptoms of a meniscus tear may include pain, especially with twisting or squatting movements, swelling, locking or catching of the knee, and limited range of motion.
The Role of Physical Therapy
Physical therapy for a meniscus tear is tailored to address the specific needs and goals of the individual. The primary objectives of physical therapy include reducing pain and inflammation, improving range of motion and strength, enhancing functional abilities, and preventing future injuries. A well-structured physical therapy program typically involves a combination of exercises, modalities, and education on proper knee mechanics and injury prevention strategies.
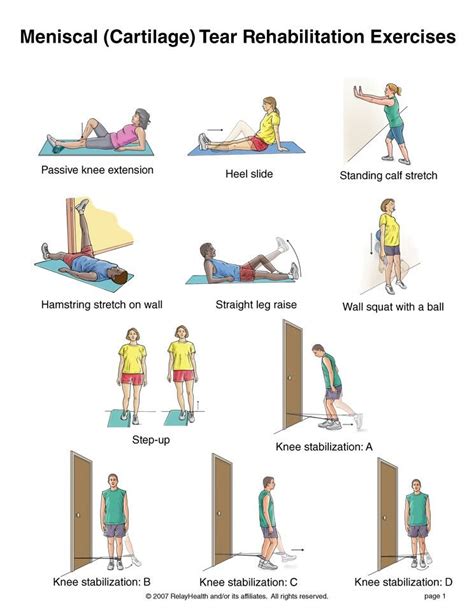
Exercises for Meniscus Tear Rehabilitation
Exercises play a pivotal role in the rehabilitation of a meniscus tear. These can be broadly categorized into several types, each serving a specific purpose:
Range of Motion Exercises: These exercises are crucial in the early stages of rehabilitation, aiming to restore normal knee movement without causing further injury to the meniscus. Examples include straight leg raises, knee bends, and wall squats.
Strengthening Exercises: As the pain and inflammation decrease, strengthening exercises become more prominent. These exercises target the muscles around the knee, such as the quadriceps and hamstrings, which are essential for knee stability and function. Examples include leg press, leg extensions, and leg curls.
Proprioception and Balance Exercises: Improving proprioception (the sense of the relative position of one’s own parts of the body) and balance is vital for preventing future knee injuries. Single-leg stance exercises, balance boards, and BOSU ball training are effective tools in this phase.
Functional Activities: As strength and stability improve, the focus shifts to functional activities that mimic daily tasks or sports-specific movements. This phase is critical for preparing the knee for the stresses of everyday life or athletic performance.
Modalities in Physical Therapy
In addition to exercises, physical therapists may employ various modalities to enhance the rehabilitation process:
- Heat and Cold Therapy: To reduce pain and inflammation.
- Electrical Stimulation: To strengthen muscles and improve healing.
- Ultrasound: To promote tissue repair and reduce inflammation.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques such as massage and joint mobilization can help improve knee mobility and reduce pain.
Education and Prevention
Education is a cornerstone of physical therapy for meniscus tears. Patients are taught about proper knee mechanics, how to avoid putting excessive stress on the meniscus, and strategies for preventing future injuries. This may include advice on appropriate footwear, training techniques, and warm-up routines.
Case Study: Meniscus Tear Rehabilitation
A 35-year-old athlete presented with a medial meniscus tear following a soccer injury. The initial phase of physical therapy focused on pain management and restoring range of motion. As symptoms improved, a progressive strengthening program was initiated, incorporating exercises such as squats, lunges, and leg press. Proprioception and balance training followed, utilizing single-leg stance exercises and balance boards. Upon achieving sufficient strength and stability, functional activities mimicking soccer movements were introduced. Post-rehabilitation, the athlete reported significant improvement in knee function and was able to return to competitive soccer without recurrence of symptoms.
Future Trends in Meniscus Tear Rehabilitation
The future of meniscus tear rehabilitation is likely to involve more personalized and technology-driven approaches. Advances in biomechanical analysis and wearable technology may provide therapists with real-time data on knee movement patterns, allowing for more precise and effective exercise prescription. Moreover, the integration of telehealth services is expected to increase accessibility to physical therapy, enabling more individuals to benefit from expert rehabilitation guidance.
Conclusion
Physical therapy stands as a cornerstone in the management of meniscus tears, offering a non-invasive and effective route to recovery. By addressing the complex needs of the knee and individual, physical therapists play a pivotal role in restoring function, reducing pain, and enhancing quality of life. As our understanding of meniscus tears and rehabilitation evolves, the integration of innovative technologies and personalized approaches will continue to reshape the landscape of physical therapy, promising improved outcomes for those affected by this common yet debilitating injury.
What are the common symptoms of a meniscus tear?
+Common symptoms include pain, especially with activities that involve twisting or squatting, swelling, catching or locking of the knee, and limited range of motion.
How long does it take to recover from a meniscus tear with physical therapy?
+Recovery time can vary significantly depending on the size and location of the tear, as well as the individual’s overall health and adherence to the physical therapy program. Generally, noticeable improvements can be seen within 6-12 weeks, but full recovery may take several months.
Can all meniscus tears be treated with physical therapy?
+Not all meniscus tears can be treated with physical therapy alone. The viability of conservative management depends on the tear’s size, location, and the patient’s symptoms. Large or complex tears may require surgical intervention, often followed by a course of physical therapy to aid in recovery.
How can I prevent meniscus tears?
+Prevention strategies include maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on the knee, engaging in regular exercise to strengthen the muscles around the knee, using proper technique during sports and activities, and incorporating exercises that improve balance and proprioception.
What role does surgery play in the treatment of meniscus tears?
+Surgery, such as arthroscopy, may be necessary for meniscus tears that are large, complex, or unlikely to heal with conservative management. The goal of surgery can be to repair the tear, remove the damaged portion of the meniscus, or in some cases, replace the meniscus with a transplant. Physical therapy often follows surgery to aid in recovery and rehabilitation.



