What Are Antithyroid Peroxidase Antibody Symptoms? Get Diagnosed

The presence of antithyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) antibodies in the blood is a common indicator of autoimmune thyroid disease, particularly Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. These antibodies are directed against the thyroid peroxidase enzyme, which plays a crucial role in the production of thyroid hormones. The symptoms associated with anti-TPO antibodies can vary widely among individuals and may not always be directly linked to the antibody levels. However, understanding these symptoms and when to seek medical attention is essential for early diagnosis and management of thyroid-related disorders.
Common Symptoms
- Fatigue and Weakness: One of the most common complaints of individuals with autoimmune thyroid disease is persistent fatigue, which can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life.
- Weight Changes: Both weight gain and weight loss can occur, depending on whether the thyroid is underactive (hypothyroidism) or overactive (hyperthyroidism). Weight gain is more common in hypothyroidism due to decreased metabolism.
- Depression and Anxiety: Mood changes, including depression and anxiety, are prevalent among individuals with thyroid autoimmunity. These can be due to the direct effects of thyroid hormone imbalance on the brain or secondary to the chronic stress of managing a chronic condition.
- Cold Intolerance: Feeling cold, even in mild temperatures, is a classic symptom of hypothyroidism, which is often associated with anti-TPO antibodies.
- Skin and Hair Changes: Dry, cool skin and hair loss are common, reflecting the decreased metabolic rate and possible nutritional deficiencies associated with thyroid dysfunction.
- Menstrual Irregularities: Women may experience changes in menstrual cycles, including heavier or lighter periods, and fertility issues, which can be related to thyroid hormone imbalances affecting the reproductive system.
- Muscle Aches and Pains: Muscle weakness and aches can occur due to the metabolic effects of thyroid hormone abnormalities on muscle tissue.
Diagnostic Process
Diagnosing anti-TPO antibody-related conditions involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and sometimes imaging studies. The process typically includes:
- Physical Examination and Medical History: A thorough examination and detailed medical history to identify symptoms and risk factors for thyroid disease.
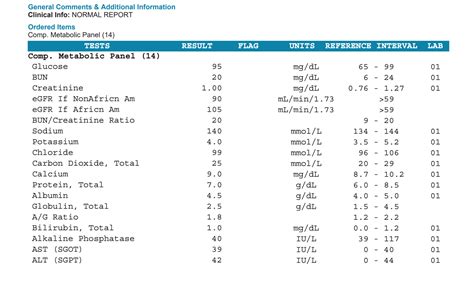
- Thyroid Function Tests (TFTs): Blood tests to measure the levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free thyroxine (FT4), and free triiodothyronine (FT3) to assess thyroid function.
- Anti-TPO Antibody Test: A specific blood test to detect the presence and levels of anti-TPO antibodies.
- Thyroid Ultrasound: In some cases, an ultrasound of the thyroid gland may be recommended to evaluate its size, structure, and the presence of any nodules.
Management and Treatment
The management of anti-TPO antibodies and related thyroid conditions is tailored to the individual’s specific needs and may involve:
- Medications: For hypothyroidism, synthetic thyroid hormone (levothyroxine) is prescribed to replace the deficient hormones. For hyperthyroidism, medications that reduce thyroid hormone production or block its effects may be used.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Dietary adjustments, stress management, and avoidance of goitrogens (substances that can interfere with thyroid function) may be recommended.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor thyroid function and adjust treatments as necessary.
Early diagnosis and appropriate management of anti-TPO antibody-related thyroid diseases can significantly improve symptoms, quality of life, and long-term outcomes. If you are experiencing symptoms that might be related to thyroid dysfunction, consulting a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and guidance is essential.
What are the most common symptoms of anti-TPO antibodies?
+The most common symptoms include fatigue, weight changes, depression, anxiety, cold intolerance, skin and hair changes, menstrual irregularities, and muscle aches and pains. These can vary widely among individuals and may not always directly correlate with antibody levels.
How are anti-TPO antibodies diagnosed?
+Diagnosis involves a physical examination, medical history, thyroid function tests (TFTs), an anti-TPO antibody test, and sometimes a thyroid ultrasound. These tests help determine the presence of anti-TPO antibodies and assess thyroid function.
What is the treatment for conditions associated with anti-TPO antibodies?
+Treatment depends on the specific condition. For hypothyroidism, synthetic thyroid hormone replacement is common. For hyperthyroidism, medications to reduce thyroid hormone production or block its effects may be prescribed. Lifestyle modifications and regular monitoring are also crucial for managing thyroid health.
Understanding and addressing the symptoms and conditions associated with anti-TPO antibodies can lead to effective management of thyroid diseases and an improved quality of life. It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan.