Intro
The Goals Against Average (GAA) formula is a crucial metric in sports, particularly in hockey, soccer, and lacrosse, to measure a goalkeeper's or team's performance. It represents the average number of goals a team or goalkeeper allows per game or per minute played. Understanding the GAA formula and its implications can provide valuable insights into a team's defensive strengths and weaknesses.
The importance of the GAA formula lies in its ability to evaluate the effectiveness of a team's defensive strategy and the performance of its goalkeeper. A lower GAA indicates that a team or goalkeeper is more effective at preventing goals, while a higher GAA suggests that they are struggling defensively. This metric is essential for coaches, analysts, and fans to assess a team's performance and make informed decisions about strategy and player development.
In addition to its practical applications, the GAA formula has a significant impact on the game itself. It can influence the way teams approach the game, with those having a low GAA often adopting a more defensive-minded strategy to protect their advantage. Conversely, teams with a high GAA may be more inclined to take risks and push for goals, knowing that they need to outscore their opponents to win. The GAA formula also affects player development, as goalkeepers and defenders strive to improve their skills and reduce their team's GAA.
Understanding the Goals Against Average Formula
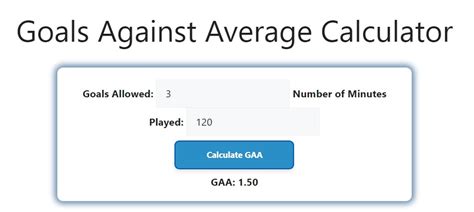
The GAA formula is calculated by dividing the total number of goals allowed by the total number of minutes played, then multiplying by the number of minutes in a game. The formula is as follows: GAA = (Total Goals Allowed / Total Minutes Played) x Minutes per Game. For example, if a team allows 20 goals in 10 games, and each game is 60 minutes long, the GAA would be (20 / 600) x 60 = 2.00.
Breaking Down the GAA Formula
The GAA formula consists of three key components: total goals allowed, total minutes played, and minutes per game. Understanding each component is essential to accurately calculate the GAA. Total goals allowed refers to the number of goals a team or goalkeeper allows during a specific period, such as a game, season, or tournament. Total minutes played represents the total amount of time a team or goalkeeper has spent playing, while minutes per game is the standard length of a game in the respective sport.Calculating the Goals Against Average
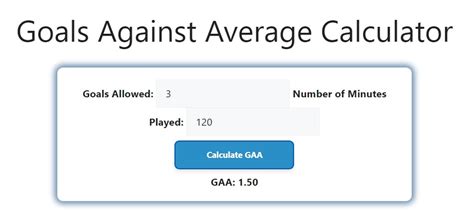
To calculate the GAA, follow these steps:
- Determine the total number of goals allowed by the team or goalkeeper.
- Calculate the total number of minutes played by the team or goalkeeper.
- Determine the number of minutes in a standard game.
- Plug the values into the GAA formula: GAA = (Total Goals Allowed / Total Minutes Played) x Minutes per Game.
Example Calculation
Suppose a hockey team allows 30 goals in 15 games, and each game is 60 minutes long. To calculate the GAA, first, determine the total minutes played: 15 games x 60 minutes per game = 900 minutes. Then, plug the values into the formula: GAA = (30 / 900) x 60 = 2.00.Interpreting the Goals Against Average
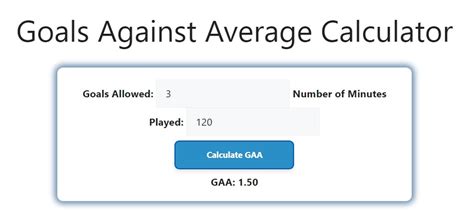
The GAA is a valuable metric for evaluating a team's or goalkeeper's performance. A lower GAA indicates a stronger defensive performance, while a higher GAA suggests a weaker defense. Here are some general guidelines for interpreting the GAA:
- A GAA of 2.00 or lower is considered excellent, indicating a strong defensive performance.
- A GAA between 2.01 and 2.50 is considered good, indicating a solid defensive performance.
- A GAA between 2.51 and 3.00 is considered average, indicating a mediocre defensive performance.
- A GAA above 3.00 is considered poor, indicating a weak defensive performance.
Factors Affecting the Goals Against Average
Several factors can influence a team's or goalkeeper's GAA, including: * The strength of the opposing teams * The team's defensive strategy and tactics * The goalkeeper's skill and experience * The team's overall performance and cohesionUsing the Goals Against Average in Decision-Making
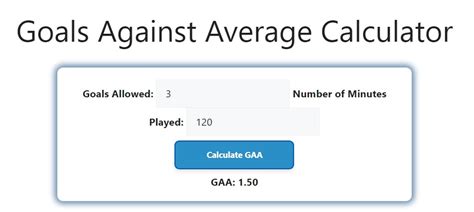
The GAA can be a useful tool for coaches, analysts, and fans to make informed decisions about strategy and player development. Here are some ways to use the GAA in decision-making:
- Evaluating a team's defensive performance and identifying areas for improvement
- Comparing the performance of different goalkeepers or defensive units
- Informing lineup decisions and strategic choices
- Assessing the effectiveness of defensive tactics and strategies
Limitations of the Goals Against Average
While the GAA is a valuable metric, it has some limitations. For example: * It does not account for the strength of the opposing teams * It does not account for the team's overall performance and cohesion * It can be influenced by external factors, such as luck and chanceConclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, the Goals Against Average formula is a powerful tool for evaluating a team's or goalkeeper's defensive performance. By understanding the formula and its implications, coaches, analysts, and fans can make informed decisions about strategy and player development. While the GAA has some limitations, it remains a valuable metric for assessing defensive performance and identifying areas for improvement.
Final Thoughts
The GAA formula is just one aspect of a team's overall performance. By considering multiple metrics and factors, coaches and analysts can gain a more comprehensive understanding of their team's strengths and weaknesses. As the sport continues to evolve, it will be interesting to see how the GAA formula is used and interpreted in the future.Goals Against Average Image Gallery
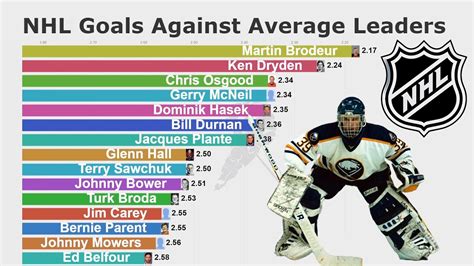
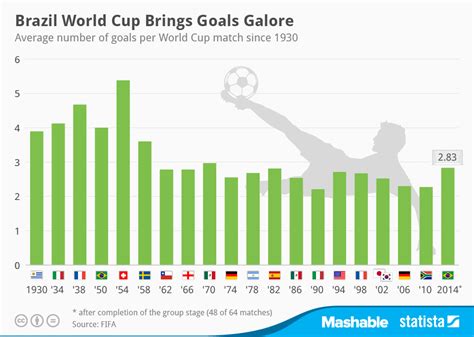






What is the Goals Against Average formula?
+The Goals Against Average formula is calculated by dividing the total number of goals allowed by the total number of minutes played, then multiplying by the number of minutes in a game.
How is the Goals Against Average used in decision-making?
+The Goals Against Average can be used to evaluate a team's defensive performance, compare the performance of different goalkeepers or defensive units, and inform lineup decisions and strategic choices.
What are the limitations of the Goals Against Average?
+The Goals Against Average has some limitations, including not accounting for the strength of the opposing teams, not accounting for the team's overall performance and cohesion, and being influenced by external factors such as luck and chance.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the Goals Against Average formula and its applications in sports. If you have any further questions or would like to share your thoughts on the topic, please don't hesitate to comment below. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with your friends and colleagues who may be interested in learning more about the Goals Against Average formula.