Intro
Discover 5 ways to graph data, including chart types, visualization tools, and graphing techniques, to effectively communicate insights and trends in data analysis and visualization.
Graphing is a fundamental concept in mathematics and science, used to visualize and analyze data. It helps in understanding the relationship between variables, identifying patterns, and making predictions. There are various methods to graph data, each with its own advantages and applications. In this article, we will explore five ways to graph, including their benefits, limitations, and examples.
Graphing is essential in many fields, including physics, engineering, economics, and computer science. It enables researchers and professionals to communicate complex ideas, identify trends, and make informed decisions. With the advancement of technology, graphing has become more accessible and efficient, allowing for the creation of interactive and dynamic visualizations. Whether you are a student, researcher, or professional, understanding the different ways to graph is crucial for effective data analysis and communication.
The importance of graphing cannot be overstated. It helps to simplify complex data, making it easier to understand and interpret. Graphs can be used to compare data, identify correlations, and visualize relationships between variables. Moreover, graphing is a powerful tool for storytelling, enabling us to convey insights and findings in a clear and concise manner. In this article, we will delve into five ways to graph, providing examples, benefits, and limitations of each method.
Introduction to Graphing
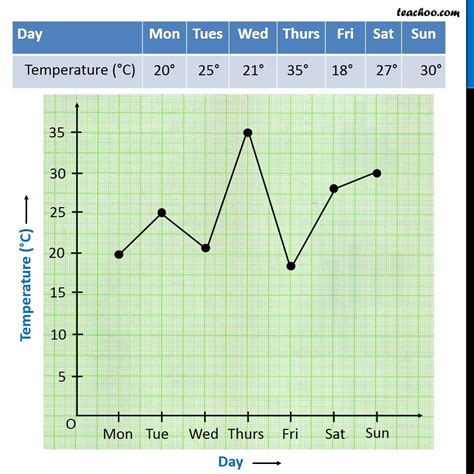
1. Line Graphs
Benefits of Line Graphs
The benefits of line graphs include: * They are easy to create and understand * They can be used to show trends and patterns * They can be used to compare data * They are commonly used in many fields, including finance, economics, and scienceLimitations of Line Graphs
The limitations of line graphs include: * They can be misleading if the data is not properly scaled * They can be difficult to read if there are too many data points * They are not suitable for displaying categorical data2. Bar Graphs
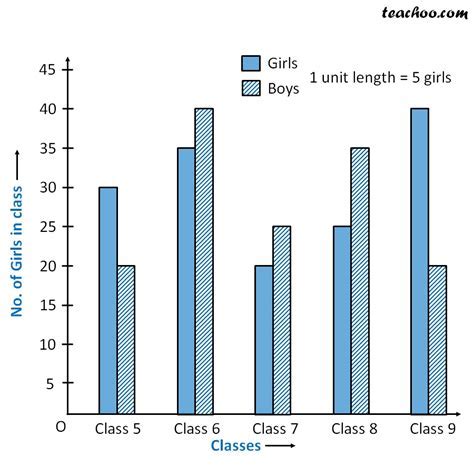
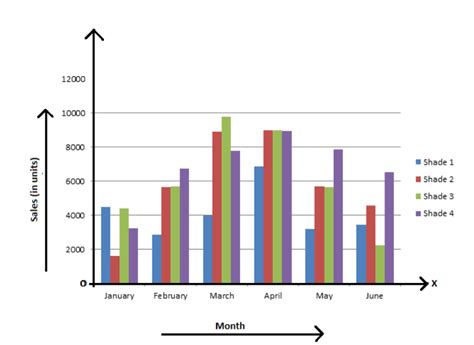
Benefits of Bar Graphs
The benefits of bar graphs include: * They are easy to create and understand * They can be used to compare data * They can be used to show differences between groups * They are commonly used in many fields, including marketing, social sciences, and educationLimitations of Bar Graphs
The limitations of bar graphs include: * They can be misleading if the data is not properly labeled * They can be difficult to read if there are too many bars * They are not suitable for displaying continuous data3. Scatter Plots
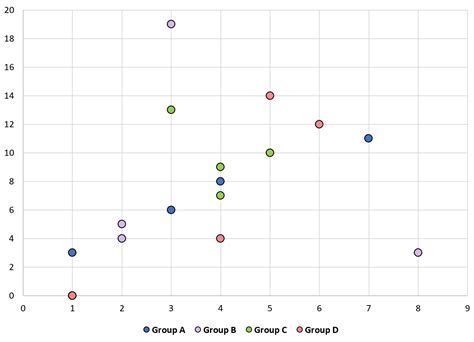
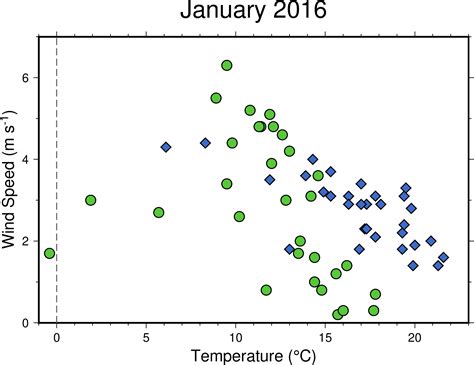
Benefits of Scatter Plots
The benefits of scatter plots include: * They can be used to show relationships between variables * They can be used to identify patterns and correlations * They are commonly used in many fields, including science, engineering, and economics * They can be used to visualize continuous dataLimitations of Scatter Plots
The limitations of scatter plots include: * They can be difficult to interpret if there are too many data points * They can be misleading if the data is not properly scaled * They are not suitable for displaying categorical data4. Histograms
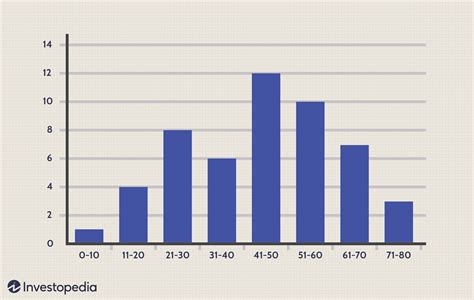
Benefits of Histograms
The benefits of histograms include: * They can be used to show the distribution of data * They can be used to identify patterns and correlations * They are commonly used in many fields, including statistics, engineering, and science * They can be used to visualize continuous dataLimitations of Histograms
The limitations of histograms include: * They can be misleading if the data is not properly binned * They can be difficult to read if there are too many bars * They are not suitable for displaying categorical data5. Pie Charts

Benefits of Pie Charts
The benefits of pie charts include: * They are easy to create and understand * They can be used to compare data * They can be used to show differences between groups * They are commonly used in many fields, including marketing, social sciences, and educationLimitations of Pie Charts
The limitations of pie charts include: * They can be misleading if the data is not properly labeled * They can be difficult to read if there are too many sectors * They are not suitable for displaying continuous dataGraphing Image Gallery

What is graphing?
+Graphing is a method of visualizing data by plotting points on a coordinate system.
What are the benefits of graphing?
+The benefits of graphing include its ability to show trends, patterns, and correlations between variables, as well as its ability to visualize continuous and categorical data.
What are the different types of graphs?
+The different types of graphs include line graphs, bar graphs, scatter plots, histograms, and pie charts, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
How do I choose the right type of graph?
+The right type of graph depends on the type of data and the purpose of the graph. For example, line graphs are suitable for showing trends, while bar graphs are suitable for comparing data.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when graphing?
+Some common mistakes to avoid when graphing include not properly labeling the axes, not scaling the data correctly, and not choosing the right type of graph for the data.
In conclusion, graphing is a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing data. The five ways to graph discussed in this article, including line graphs, bar graphs, scatter plots, histograms, and pie charts, each have their own strengths and weaknesses. By understanding the benefits and limitations of each type of graph, you can choose the right type of graph for your data and effectively communicate your findings. Whether you are a student, researcher, or professional, graphing is an essential skill that can help you to better understand and analyze data. We encourage you to share this article with others, ask questions, and explore the different types of graphs to improve your graphing skills.