Intro
Understanding and working with map elements is crucial for navigation, geography, and even everyday life. Maps have been a cornerstone of human exploration and discovery, allowing us to visualize and interact with our surroundings in a meaningful way. The importance of map elements cannot be overstated, as they provide the necessary information for us to understand the layout of an area, locate specific places, and plan routes. Whether you're a student, a traveler, or simply someone interested in geography, grasping the basics of map elements is essential.
The ability to read and interpret maps is a skill that has been passed down through generations. From the early days of cartography, where maps were painstakingly drawn by hand, to the modern era of digital mapping, the core elements of maps have remained relatively consistent. These elements include symbols, keys, scales, and grids, among others. Each of these components plays a vital role in ensuring that a map is both informative and easy to use. For instance, symbols help to represent different features such as roads, buildings, and bodies of water, while a key or legend explains what each symbol means. The scale of a map allows users to understand the relationship between distances on the map and real-world distances, which is crucial for planning journeys or estimating travel times.
In today's world, where technology has made it possible to access maps on our smartphones and computers, the need to understand map elements has not diminished. In fact, with the rise of GPS navigation and online mapping services, being able to interpret map data has become more important than ever. Whether you're using a physical map to navigate through a new city or relying on a digital map to find your way, the principles of map reading remain the same. It's about understanding how to use the various elements of a map to gather information, make decisions, and ultimately reach your destination.
Introduction to Map Elements

Map elements are the building blocks of any map. They are the components that, when combined, provide a comprehensive view of an area. These elements can be broadly categorized into several types, including title, legend, scale, grid, and symbols. Each of these elements serves a specific purpose and contributes to the overall utility of the map. For example, the title of a map tells you what area the map covers, while the legend explains the meaning of the symbols used. The scale helps you understand the size of the area represented by the map, and the grid system allows you to pinpoint exact locations.
Types of Map Elements
Understanding the different types of map elements is crucial for effective map reading. Here are some of the key elements you'll find on most maps: - **Title:** The title tells you the name of the map and what area it represents. - **Legend (Key):** The legend explains the symbols and colors used on the map. - **Scale:** The scale shows the relationship between distances on the map and real-world distances. - **Grid System:** Many maps use a grid system to help you locate specific places. - **Symbols:** Symbols are used to represent different features on the map, such as roads, buildings, and bodies of water.Working with Map Scales
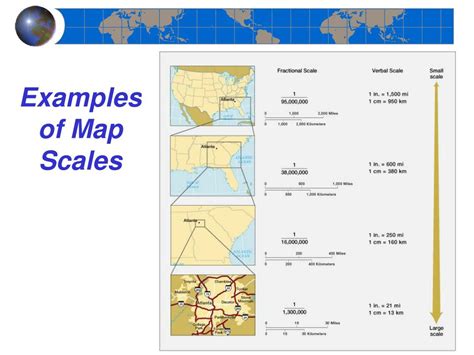
Map scales are a critical component of any map. They provide a way to measure distances and understand the size of the area represented by the map. There are two main types of scales: ratio scales and verbal scales. A ratio scale is a graphical scale that represents the relationship between the size of the map and the size of the real world. It's usually a line divided into segments, with each segment representing a certain distance. On the other hand, a verbal scale uses words to describe the scale. For example, it might say "1 inch represents 1 mile."
Using Map Scales for Navigation
To use a map scale for navigation, follow these steps: 1. **Identify the Scale:** Look for the scale on the map. It might be represented as a ratio (e.g., 1:50,000) or as a verbal description. 2. **Understand the Scale:** Make sure you understand what the scale means. For example, if the scale is 1:50,000, this means that 1 unit on the map represents 50,000 units in real life. 3. **Measure Distances:** Use the scale to measure distances on the map. This can help you estimate how far apart places are and how long it might take to travel between them.Map Symbols and Legends

Map symbols and legends are essential for interpreting the information presented on a map. Symbols are used to represent different features such as roads, rivers, and buildings, while the legend explains what each symbol means. The legend is essentially a key that deciphers the code of symbols used on the map, allowing users to understand the map's contents fully.
Common Map Symbols
Here are some common map symbols you might encounter: - **Roads and Highways:** These are usually represented by lines of varying thickness and color, with thicker lines indicating more important roads. - **Bodies of Water:** Rivers, lakes, and oceans are often depicted in blue. - **Buildings and Structures:** These can be represented by a variety of symbols, depending on their type and importance.Grid Systems on Maps

Grid systems are used on maps to help locate specific places. The most common type of grid system is the latitude and longitude system, which divides the Earth into a series of parallel and perpendicular lines. However, maps can also use other types of grid systems, such as the Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) system, which is more complex but provides more precise location information.
Using Grid Systems for Location
To use a grid system for location, follow these steps: 1. **Identify the Grid:** Look for the grid lines on the map. These are usually marked with coordinates or other reference points. 2. **Understand the Grid:** Make sure you understand how the grid system works. For example, if you're using latitude and longitude, you'll need to know how to read these coordinates. 3. **Find Your Location:** Use the grid system to find your location on the map. This can involve reading the coordinates of your location or using the grid lines to estimate your position.Map Elements Image Gallery




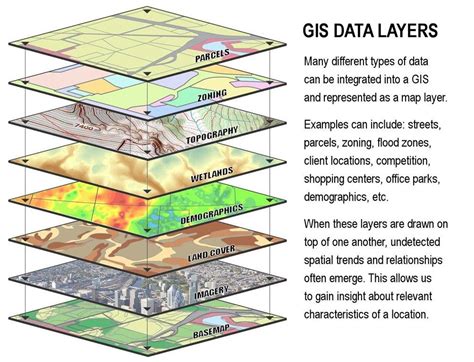


What are the basic elements of a map?
+The basic elements of a map include the title, legend, scale, grid system, and symbols. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in helping users understand and navigate the map.
How do I use a map scale to measure distances?
+To use a map scale, first identify the scale on the map. Then, understand what the scale represents. For example, if the scale is 1:50,000, this means 1 unit on the map represents 50,000 units in real life. Use a ruler or other measuring device to measure the distance between two points on the map, and then convert this measurement to real-world distances using the scale.
What is the purpose of a legend on a map?
+The legend, or key, on a map explains the meaning of the symbols, colors, and other markings used on the map. It helps users understand what they are looking at and provides a reference for interpreting the map's contents.
In conclusion, understanding map elements is vital for anyone looking to navigate the world effectively, whether that's through physical maps or digital applications. By grasping the basics of map reading, including scales, symbols, legends, and grid systems, individuals can unlock a wealth of information that can aid in exploration, travel, and even everyday decision-making. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of these fundamental skills will only continue to grow, making it essential for people of all ages to learn and practice map reading. So, take the first step today and start exploring the world around you with confidence and precision. Share your thoughts on the importance of map elements in the comments below, and don't forget to share this guide with anyone who might find it useful. Together, let's navigate the world with ease and accuracy.