Intro
The ability to effectively combine graphs is a crucial skill in data analysis and visualization. By merging different types of graphs, analysts can provide a more comprehensive view of the data, facilitating better understanding and decision-making. In this article, we will delve into the importance of graph combination, its benefits, and provide practical examples to guide readers through the process.
Combining graphs allows for the presentation of complex data in a more digestible format. It enables the comparison of different data sets, trends, and patterns, which can be particularly useful in fields such as business, science, and economics. Moreover, when graphs are combined thoughtfully, they can significantly enhance the visual appeal of a presentation or report, making it more engaging for the audience.
The process of combining graphs requires careful consideration of the types of graphs being used, the nature of the data, and the story that the analyst wants to tell. Different types of graphs serve different purposes; for example, line graphs are ideal for showing trends over time, while bar graphs are better suited for comparing categorical data. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each graph type, analysts can select the most appropriate combinations to convey their message effectively.
Introduction to Graph Combination
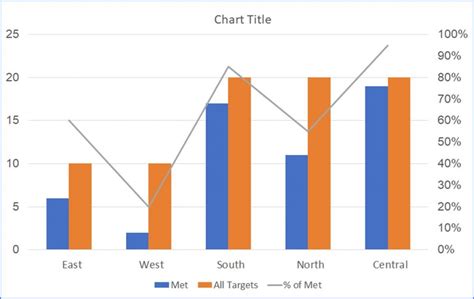
Combining graphs can be as simple as placing two or more graphs side by side or as complex as overlaying different types of graphs on the same set of axes. The key to successful graph combination is ensuring that the resulting visualizations are clear, intuitive, and easy to interpret. This involves selecting appropriate scales, colors, and labels, as well as avoiding unnecessary complexity.
Benefits of Combining Graphs
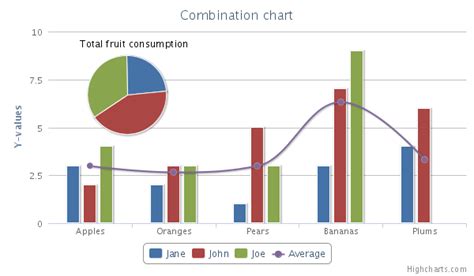
The benefits of combining graphs are numerous. Firstly, it allows for a more holistic understanding of the data by presenting multiple facets of the information in a single view. This can lead to insights that might not be apparent from looking at individual graphs in isolation. Secondly, combined graphs can reduce the clutter and complexity associated with presenting multiple separate graphs, making the overall presentation more concise and easier to follow.
Types of Graph Combinations
There are several ways to combine graphs, each suited to different types of data and analytical goals. These include: - **Overlaying Graphs**: Placing one graph over another, often used for comparing trends or distributions. - **Side-by-Side Graphs**: Presenting two or more graphs next to each other, useful for direct comparisons. - **Stacked Graphs**: Combining multiple graphs into a single graph where each component is stacked on top of the others, typically used for showing how different categories contribute to a whole. - **Interactive Graphs**: Using digital tools to create graphs that can be manipulated by the viewer, such as zooming in or hovering over data points for more information. - **3D Graphs**: Representing data in three dimensions, which can be useful for visualizing complex relationships but requires careful use to avoid visual confusion.Steps to Combine Graphs Effectively
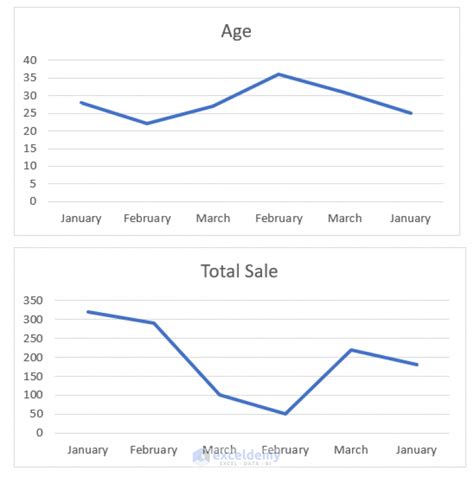
To combine graphs effectively, follow these steps:
- Define Your Objective: Clearly determine what you want to achieve with your combined graph. What story do you want to tell with your data?
- Select Appropriate Graph Types: Choose graph types that best represent the data and facilitate the comparison or analysis you wish to perform.
- Ensure Consistency: Use consistent scales, colors, and labeling across graphs to make comparisons easier.
- Avoid Clutter: Keep the design clean and simple. Too much information can overwhelm the viewer and obscure the message.
- Test and Refine: Review your combined graph for clarity and effectiveness, making adjustments as necessary.
Tools for Combining Graphs
Various tools and software are available for creating and combining graphs, ranging from basic spreadsheet programs like Microsoft Excel to specialized data visualization tools such as Tableau, Power BI, and D3.js. The choice of tool depends on the complexity of the graphs, the size and nature of the data, and the desired level of interactivity.Best Practices for Graph Combination
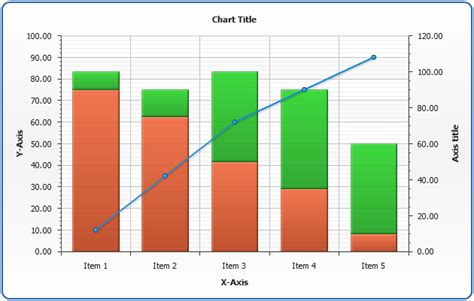
Best practices include using color effectively to differentiate between data sets, ensuring that axes and labels are clear and well-explained, and providing a legend or key when necessary. It's also important to consider the audience and tailor the complexity and detail of the combined graphs accordingly.
Common Challenges and Solutions
One common challenge is dealing with data sets of vastly different scales. A solution is to use logarithmic scales or to normalize the data. Another challenge is ensuring that the combined graph does not become too complex or confusing. This can be addressed by carefully selecting which data to include and how to present it, often through iterative refinement.Real-World Applications of Combined Graphs
Combined graphs have numerous real-world applications. In business, they can be used to compare sales trends across different regions or product lines. In science, they can help illustrate the relationship between different variables or the impact of an experiment. In economics, combined graphs can show trends in employment, inflation, and GDP over time, providing valuable insights for policymakers.
Future of Graph Combination
The future of graph combination is closely tied to advancements in data visualization technology and the increasing availability of large, complex data sets. As tools become more sophisticated, we can expect to see more interactive, dynamic, and immersive graph combinations that facilitate deeper insights and more effective communication of data-driven stories.Gallery of Combined Graph Examples
Combined Graph Image Gallery

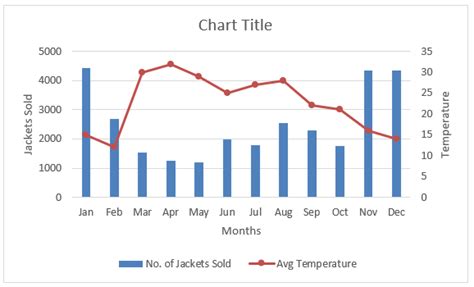
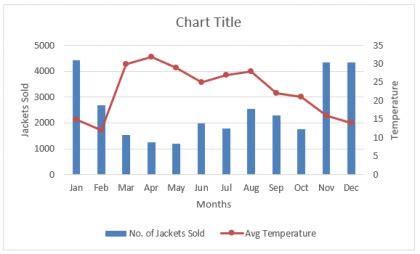
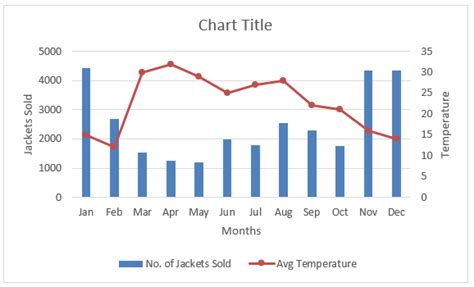
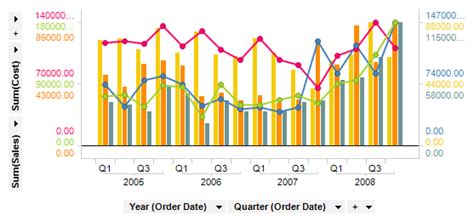
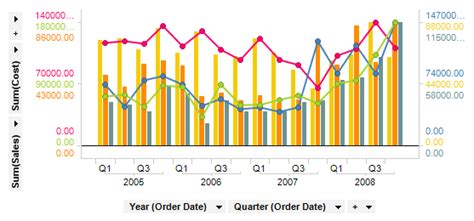
What is the primary benefit of combining graphs?
+The primary benefit of combining graphs is that it allows for a more comprehensive view of the data, facilitating better understanding and decision-making by presenting multiple facets of the information in a single view.
How do I choose the right types of graphs to combine?
+Choosing the right types of graphs to combine depends on the nature of the data and the story you want to tell. For example, line graphs are ideal for showing trends over time, while bar graphs are better suited for comparing categorical data.
What are some common challenges when combining graphs?
+Common challenges include dealing with data sets of vastly different scales and ensuring that the combined graph does not become too complex or confusing. Solutions include using logarithmic scales, normalizing the data, and carefully selecting which data to include and how to present it.
In conclusion, combining graphs is a powerful technique for data analysis and visualization, offering a way to present complex information in a clear and compelling manner. By understanding the different types of graph combinations, their applications, and the best practices for their creation, individuals can leverage this technique to communicate insights more effectively. Whether in academia, business, or any field that relies on data-driven decision-making, the ability to combine graphs will continue to play a vital role in uncovering and presenting valuable insights. We invite readers to share their experiences and tips on combining graphs, and to explore the many tools and resources available for enhancing data visualization skills.