Intro
Learn to randomize order in Excel using formulas and functions, including RAND and RANDBETWEEN, to shuffle data and create random lists, perfect for data analysis and simulation tasks.
Randomizing the order of data in Excel can be useful for various purposes, such as creating random samples, shuffling data for presentations, or even for lottery-style drawings. Excel provides several methods to achieve this, including using formulas, the "Data" tab, and VBA scripts. Here, we'll explore some of the most straightforward and commonly used methods.
The importance of randomizing data cannot be overstated, especially in statistical analysis and research. It helps in reducing bias and ensuring that the sample is representative of the population. Moreover, in educational settings, randomizing questions or data can make quizzes and assessments more engaging and challenging. Whether you're a student, researcher, or professional, knowing how to randomize data in Excel is a valuable skill.
For those who are new to Excel or have limited experience with data manipulation, the process might seem daunting. However, Excel's user-friendly interface and powerful functions make it easier than you think. With a few simple steps, you can randomize your data and unlock new possibilities for analysis and presentation. So, let's dive into the methods of randomizing data in Excel and explore the benefits and applications of this versatile skill.
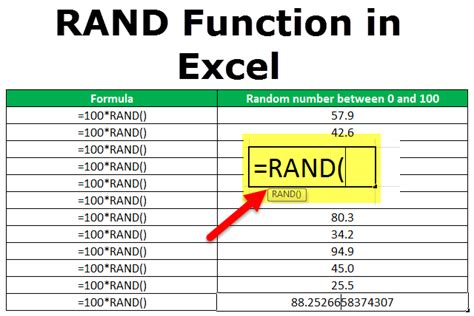
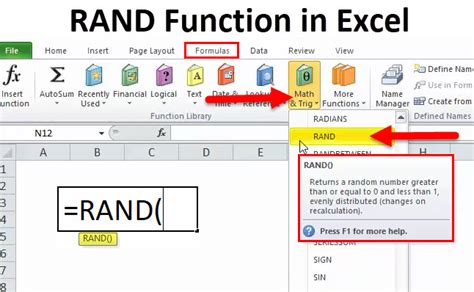
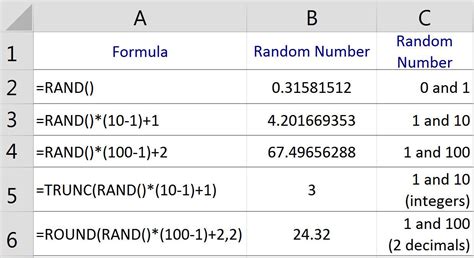
Using the RAND Function
Using the Shuffle Feature in Excel

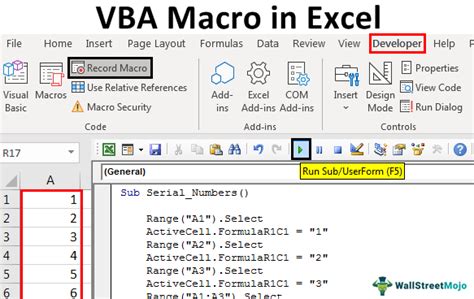
Using VBA Macros
LastRow = Cells(Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
For i = 1 To LastRow
For j = i + 1 To LastRow
If Rnd() < 0.5 Then
Temp = Cells(i, 1).Value
Cells(i, 1).Value = Cells(j, 1).Value
Cells(j, 1).Value = Temp
End If
Next j
Next i
End Sub
- Save the module by clicking "File" > "Save" (or press Ctrl + S).
- Close the VBA Editor and return to your Excel worksheet.
- Press Alt + F8 to open the Macro dialog box, select `ShuffleData`, and click "Run".
Benefits of Randomizing Data
Randomizing data offers several benefits, including:
- **Reduced Bias**: Randomization helps ensure that your sample is representative of the population, reducing bias in statistical analyses.
- **Improved Generalizability**: By shuffling your data, you can increase the generalizability of your findings to the larger population.
- **Enhanced Privacy**: In some cases, randomizing data can help protect sensitive information by making it more difficult to identify individual data points.
Practical Applications
The ability to randomize data in Excel has numerous practical applications across various fields:
- **Research and Statistics**: For creating random samples, reducing bias, and ensuring the representativeness of the data.
- **Education**: For generating random quizzes, assignments, or assessments to keep students engaged.
- **Marketing and Sales**: For randomizing customer lists to select participants for surveys or promotions.
Randomization Techniques Image Gallery


What is the purpose of randomizing data in Excel?
+
The purpose of randomizing data in Excel is to reduce bias, improve the generalizability of findings, and enhance privacy by making individual data points less identifiable.
How do I randomize data using the RAND function in Excel?
+
To randomize data using the RAND function, enter `=RAND()` in a new column next to your data, copy the formula down for all rows, and then sort your data based on this column.
Can I use VBA macros to randomize data in Excel?
+
Yes, you can use VBA macros to randomize data in Excel. This involves creating a macro that shuffles the data in your selected range.
What are the benefits of using the Power Query feature for randomizing data?
+
The Power Query feature allows for more complex data manipulation, including randomization, and can be particularly useful for large datasets or when you need to perform the randomization repeatedly.
How often should I randomize my data for statistical analysis?
+
The frequency of randomizing data for statistical analysis depends on the nature of your study and the requirements of your methodology. It's essential to consult with a statistician or refer to relevant methodological guidelines for your specific field of research.
In conclusion, randomizing data in Excel is a powerful tool that can enhance the validity and reliability of your analyses, presentations, and research. Whether you're using the RAND function, the Power Query feature, or VBA macros, Excel provides a range of methods to suit different needs and preferences. As you explore these techniques, remember to consider the context and purpose of your data randomization to ensure that you're using the most appropriate method for your specific requirements. If you have any questions or need further clarification on any of the methods discussed, feel free to comment below. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please share it with others who might benefit from learning about randomizing data in Excel.