Intro
Running queries in VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) is a powerful way to interact with databases, perform data analysis, and automate tasks. VBA is commonly used in Microsoft Office applications such as Excel, Access, and Word. Here, we'll explore five ways to run queries in VBA, focusing on Excel and Access, as these are the most relevant applications for database interactions and data manipulation.
The ability to execute queries is essential for extracting, transforming, and loading data (ETL processes), data analysis, and reporting. Whether you're working with internal databases, external data sources, or even just manipulating data within Excel worksheets, understanding how to run queries in VBA can significantly enhance your productivity and the efficiency of your workflows.
Introduction to Running Queries in VBA
Before diving into the methods, it's crucial to understand the basics of VBA and how queries can be integrated into VBA scripts. Queries in VBA can be used to fetch data from databases, perform calculations, and update records. The most common types of queries include SELECT (to retrieve data), INSERT (to add new records), UPDATE (to modify existing records), and DELETE (to remove records).
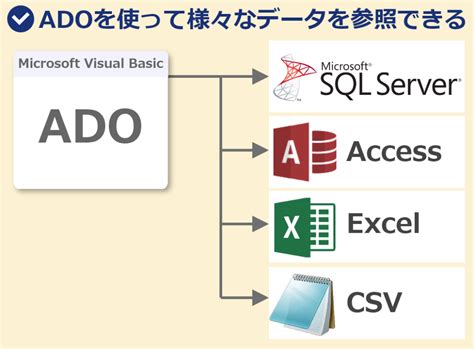
Method 1: Using ADO (ActiveX Data Objects)
ADO is a set of COM components that allow you to access data stored in a variety of formats, including relational databases, ISAM/VSAM databases, and even text files. To use ADO in VBA, you need to set a reference to the ADO library in your VBA editor.
Sub RunQueryUsingADO()
Dim cn As ADODB.Connection
Dim rs As ADODB.Recordset
Dim strSQL As String
' Create a connection object
Set cn = New ADODB.Connection
' Set the connection string
cn.Open "Provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0;Data Source=C:\YourDatabase.accdb"
' Define your SQL query
strSQL = "SELECT * FROM YourTable"
' Create a recordset object
Set rs = New ADODB.Recordset
' Open the recordset
rs.Open strSQL, cn
' Do something with the data, e.g., print it
While Not rs.EOF
Debug.Print rs!FieldName
rs.MoveNext
Wend
' Clean up
rs.Close
Set rs = Nothing
cn.Close
Set cn = Nothing
End Sub
Method 2: Using DAO (Data Access Object)
DAO is another library that allows VBA to interact with databases. It's particularly useful for working with Access databases.
Sub RunQueryUsingDAO()
Dim db As DAO.Database
Dim rs As DAO.Recordset
Dim strSQL As String
' Open the database
Set db = OpenDatabase("C:\YourDatabase.accdb")
' Define your SQL query
strSQL = "SELECT * FROM YourTable"
' Open the recordset
Set rs = db.OpenRecordset(strSQL, dbOpenSnapshot)
' Do something with the data
While Not rs.EOF
Debug.Print rs!FieldName
rs.MoveNext
Wend
' Clean up
rs.Close
Set rs = Nothing
db.Close
Set db = Nothing
End Sub
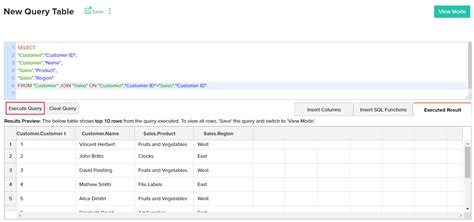
Method 3: Using Excel’s QueryTable Object
For Excel users, the QueryTable object provides an easy way to fetch data from external sources, including databases.
Sub RunQueryUsingQueryTable()
Dim qt As QueryTable
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("YourSheet")
' Delete any existing query tables
For Each qt In ws.QueryTables
qt.Delete
Next qt
' Create a new query table
Set qt = ws.QueryTables.Add(Connection:="OLEDB;Provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0;Data Source=C:\YourDatabase.accdb", Destination:=ws.Range("A1"))
' Define your SQL query
qt.CommandText = "SELECT * FROM YourTable"
' Refresh the query table
qt.Refresh BackgroundQuery:=False
Set qt = Nothing
Set ws = Nothing
End Sub
Method 4: Using Excel’s Workbook Connections
Excel allows you to create connections to external data sources, which can then be used to run queries.
Sub RunQueryUsingWorkbookConnections()
Dim oCn As WorkbookConnection
For Each oCn In ThisWorkbook.Connections
oCn.Delete
Next oCn
' Create a new connection
With ThisWorkbook.Connections.Add2("YourConnection", _
"OLEDB;Provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0;Data Source=C:\YourDatabase.accdb", _
"SELECT * FROM YourTable", "YourRange", 7, True, False)
End With
' Refresh all connections
ThisWorkbook.Connections("YourConnection").Refresh
Set oCn = Nothing
End Sub

Method 5: Using SQL in Access VBA
For Access users, you can execute SQL queries directly within VBA.
Sub RunQueryInAccessVBA()
Dim db As DAO.Database
Dim strSQL As String
Set db = CurrentDb()
' Define your SQL query
strSQL = "SELECT * FROM YourTable"
' Execute the query
db.Execute strSQL, dbFailOnError
Set db = Nothing
End Sub

Gallery of VBA Query Examples
VBA Query Examples Gallery
FAQs
What is VBA used for in running queries?
+VBA is used to automate tasks, interact with databases, and perform data analysis by running queries.
How do I connect to a database in VBA?
+You can connect to a database using ADO or DAO libraries in VBA, by setting a connection string that specifies the provider, data source, and other necessary details.
What types of queries can I run in VBA?
+You can run SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE queries, among others, depending on your database and the actions you wish to perform.
To further explore the capabilities of running queries in VBA, consider experimenting with different types of queries, connecting to various data sources, and automating tasks within your applications. The flexibility and power of VBA, combined with its ability to interact with databases and external data sources, make it an invaluable tool for data professionals and automation specialists alike. Whether you're looking to enhance your data analysis skills, automate repetitive tasks, or simply explore the potential of VBA, the world of query execution in VBA is rich with possibilities and applications.