Intro
Master Excel calculations with 5 ways to calculate EMA, including exponential moving average formulas, charting, and data analysis techniques for precise stock market trends and forecasting using Excel tools and functions.
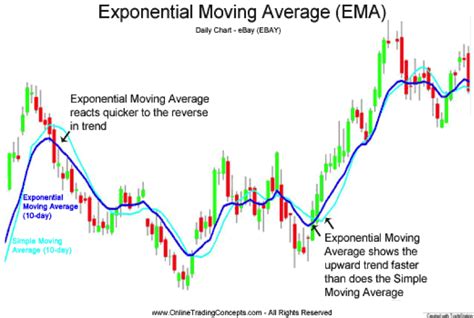
Calculating the Exponential Moving Average (EMA) in Excel is a valuable skill for anyone involved in financial analysis, trading, or investing. The EMA is a type of moving average that gives more weight to the most recent data points, making it a popular tool for smoothing out price data and highlighting trends. Here, we'll explore five ways to calculate EMA in Excel, each with its own advantages and applications.
The importance of understanding how to calculate EMA in Excel cannot be overstated. It allows users to analyze historical data, predict future trends, and make informed decisions based on quantitative analysis. Whether you're a seasoned financial analyst or just starting to learn about technical indicators, mastering the EMA calculation is a crucial step. In this article, we'll delve into the world of EMA calculations, providing a comprehensive guide on how to implement them in Excel.
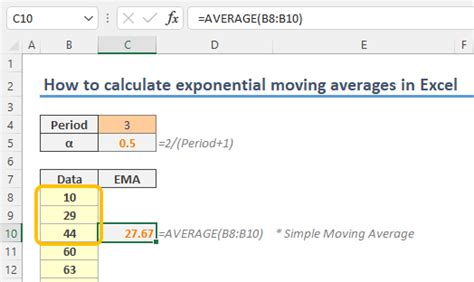
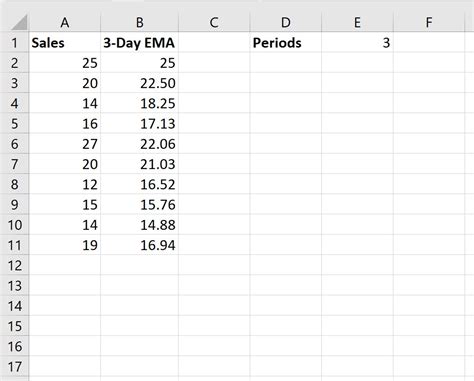
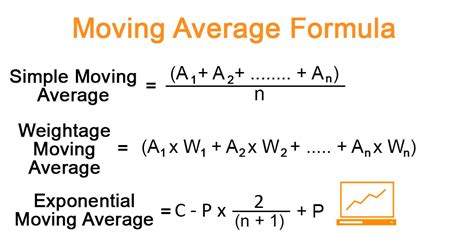
Before we dive into the methods, it's essential to understand the basic formula for calculating EMA. The formula for EMA is: EMA = (Close * (Smoothing / 1 + Days)) + EMAprevious * (1 - (Smoothing / 1 + Days)), where "Close" is the current closing price, "Smoothing" is the smoothing factor (usually 2), and "Days" is the number of days for the moving average. The "EMApervious" refers to the previous EMA value. This formula will be the foundation for our calculations.
Method 1: Using the EMA Formula Directly
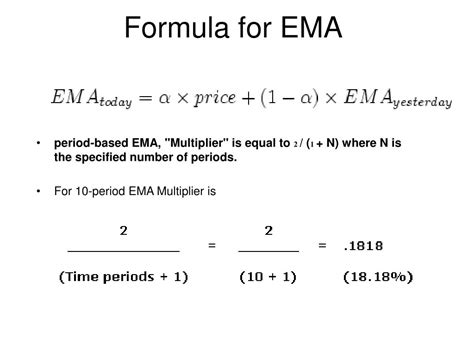
Method 2: Creating a User-Defined Function (UDF)
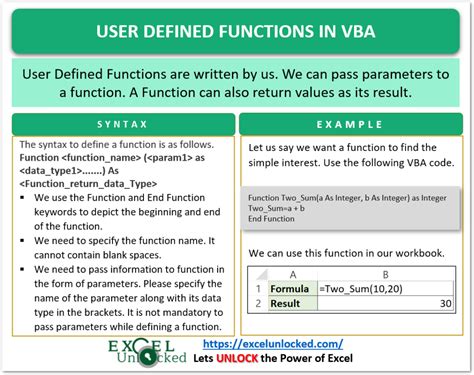
Method 3: Utilizing Excel's Built-in Functions
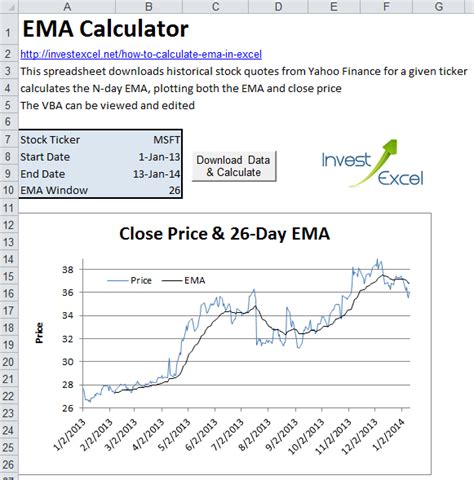
Method 4: Using Add-ins or Third-Party Tools

Method 5: Array Formula for Dynamic EMA Calculation
Gallery of EMA Calculations in Excel
EMA Calculation Methods

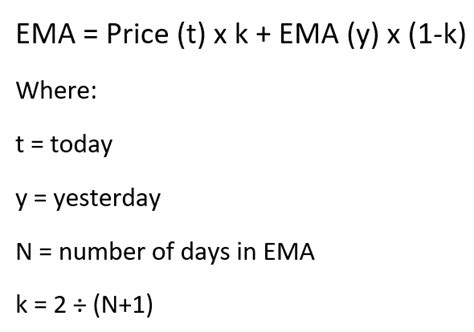
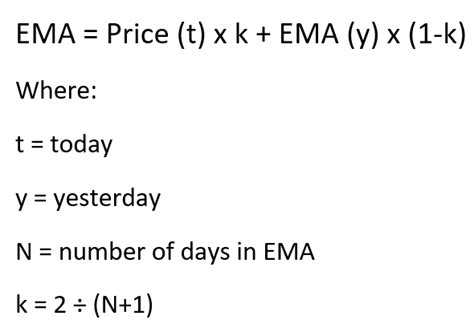
What is the primary difference between EMA and SMA?
+The primary difference is that EMA gives more weight to recent prices, whereas SMA gives equal weight to all prices in the period.
How do I choose the right period for my EMA calculation?
+The choice of period depends on your trading strategy and the market you're analyzing. Shorter periods are more sensitive to price changes, while longer periods smooth out fluctuations.
Can I use EMA for other types of data analysis beyond finance?
+Yes, the EMA can be applied to any time-series data to highlight trends and smooth out fluctuations, making it useful in various fields beyond finance.
In conclusion, calculating the Exponential Moving Average in Excel is a versatile skill that can enhance your data analysis capabilities. Whether you're a financial analyst, trader, or simply interested in understanding trends, mastering the EMA calculation can provide valuable insights. By exploring the different methods outlined in this article, you can choose the approach that best fits your needs and skill level. Remember, practice makes perfect, so don't hesitate to experiment with these methods on your own datasets. Share your experiences, ask questions, and explore how EMA calculations can benefit your work or personal projects.