Intro
The importance of understanding and addressing return blanks in various contexts cannot be overstated. Return blanks, or the absence of expected data or responses, can significantly impact decision-making, analysis, and outcomes in fields such as business, research, and technology. This phenomenon can arise from a multitude of factors, including errors in data collection, misunderstandings in communication, or the intentional withholding of information. As we delve into the complexities of return blanks, it becomes clear that there are several key strategies and perspectives that can help mitigate their effects and improve overall efficiency and understanding.
One of the primary challenges posed by return blanks is the potential for misinterpretation or the drawing of incorrect conclusions based on incomplete data. In many cases, the absence of a response or the presence of blank fields in datasets can lead to biases in analysis or the failure to identify critical patterns and trends. Furthermore, return blanks can also reflect systemic issues, such as flaws in survey design, inadequate communication channels, or technical glitches, which, if left unaddressed, can perpetuate inefficiencies and hinder progress.
The impact of return blanks is not limited to any one sector; rather, it is a pervasive issue that can affect everything from market research and customer feedback analysis to medical studies and governmental surveys. For instance, in the context of market research, return blanks can skew perceptions of consumer preferences and behaviors, potentially leading to misguided product development and marketing strategies. Similarly, in medical research, missing data can complicate the assessment of treatment efficacy and patient outcomes, thereby influencing healthcare policy and practice.
Understanding Return Blanks

To effectively address return blanks, it is essential to understand their underlying causes and the contexts in which they occur. This involves a thorough examination of the data collection processes, the design of surveys and questionnaires, and the communication strategies employed. By identifying the root causes of return blanks, individuals and organizations can develop targeted interventions to minimize their occurrence and mitigate their impact.
Causes of Return Blanks
The causes of return blanks can be diverse and multifaceted. Some common factors include: - Lack of clarity or relevance in the questions being asked - Insufficient incentives for respondents to provide complete and accurate information - Technical issues or difficulties in accessing the data collection platform - Respondent fatigue or lack of engagement due to lengthy or complex surveys - Cultural or language barriers that hinder effective communicationStrategies for Addressing Return Blanks

Several strategies can be employed to address return blanks and enhance the quality and completeness of data. These include:
- Improving Survey Design: Ensuring that surveys are well-designed, concise, and relevant to the target audience can significantly reduce return blanks. This involves piloting surveys, using clear and simple language, and making sure that the questions are engaging and pertinent.
- Enhancing Communication: Effective communication is crucial for minimizing return blanks. This can involve providing clear instructions, offering support for respondents, and ensuring that the purpose and benefits of the data collection effort are well-understood.
- Utilizing Technology: Leveraging technology, such as online survey tools and data analytics software, can help identify and address return blanks more efficiently. Automated reminders, for example, can encourage respondents to complete surveys, while data validation checks can help detect and correct errors in real-time.
- Incentivizing Responses: Offering incentives, whether they be monetary, informational, or reciprocal in nature, can motivate respondents to provide complete and accurate information, thereby reducing return blanks.
- Implementing Follow-Up Procedures: Establishing follow-up procedures for non-respondents or partial respondents can help capture missing data and reduce the incidence of return blanks. This might involve sending reminders, making personal contacts, or using alternative data collection methods.
Best Practices for Data Analysis
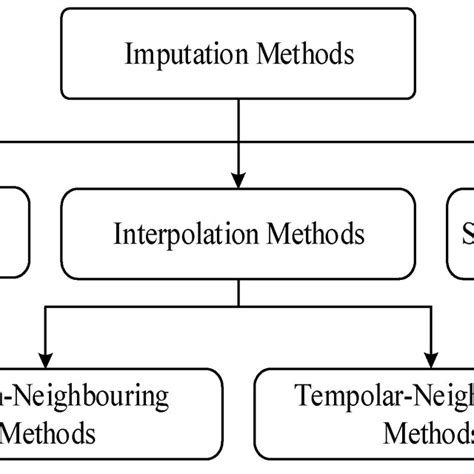
When dealing with datasets that contain return blanks, it is vital to employ best practices in data analysis to ensure that conclusions drawn are reliable and unbiased. This includes: - **Imputation Techniques**: Using statistical methods to impute missing values can help maintain the integrity of the dataset and support more accurate analysis. - **Sensitivity Analysis**: Conducting sensitivity analysis to understand how different approaches to handling return blanks affect the outcomes of the analysis can provide valuable insights and enhance the robustness of the findings. - **Transparent Reporting**: Clearly documenting the presence of return blanks, the methods used to address them, and the potential implications for the analysis is essential for maintaining transparency and credibility.Gallery of Return Blanks
Return Blanks Image Gallery







Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary causes of return blanks in data collection?
+The primary causes of return blanks include poor survey design, lack of clear communication, technical issues, and respondent fatigue or disengagement.
How can return blanks be addressed in data analysis?
+Return blanks can be addressed through the use of imputation techniques, sensitivity analysis, and transparent reporting of methods and limitations.
What strategies can be employed to minimize return blanks in surveys?
+Strategies to minimize return blanks include improving survey design, enhancing communication, utilizing technology, incentivizing responses, and implementing follow-up procedures for non-respondents.
In wrapping up our exploration of return blanks, it is evident that these gaps in data or responses present significant challenges across various domains. However, by understanding their causes, employing effective strategies to address them, and adopting best practices in data analysis, individuals and organizations can mitigate the impacts of return blanks and foster more informed decision-making. We invite readers to share their experiences and insights regarding return blanks, and we look forward to continuing the conversation on this critical topic. Whether you are a researcher seeking to improve the accuracy of your findings, a business leader aiming to enhance customer engagement, or simply an individual interested in the complexities of data collection and analysis, your thoughts and questions are invaluable in helping us navigate the complexities of return blanks and strive for excellence in our pursuits.