Intro
Discover 5 ways link cells enhance spreadsheet functionality, including data consolidation, formula referencing, and dynamic updates, using link cell techniques for efficient data management and analysis.
The importance of understanding how cells communicate and interact with each other cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including development, tissue repair, and immune responses. One key aspect of cell communication is the formation of links between cells, which enables them to share information, coordinate their behavior, and maintain tissue structure. In this article, we will delve into the world of cell biology and explore the different ways in which cells can link together, with a focus on the 5 ways link cells.
Cell communication is a complex process that involves various mechanisms, including direct cell-to-cell contact, signaling pathways, and the release of chemical messengers. The ability of cells to communicate with each other is essential for maintaining tissue homeostasis, responding to changes in the environment, and coordinating the behavior of different cell types. One of the key ways in which cells communicate is through the formation of cell-cell junctions, which provide a physical link between adjacent cells and enable them to share information and coordinate their behavior.
The study of cell-cell junctions has revealed a complex and highly regulated process that involves the coordination of multiple cellular components, including adhesion molecules, signaling pathways, and cytoskeletal elements. Understanding how cells link together is essential for understanding various biological processes, including development, tissue repair, and disease. In this article, we will explore the 5 ways link cells, including adherens junctions, tight junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions, and synaptic junctions.
Introduction to Cell-Cell Junctions
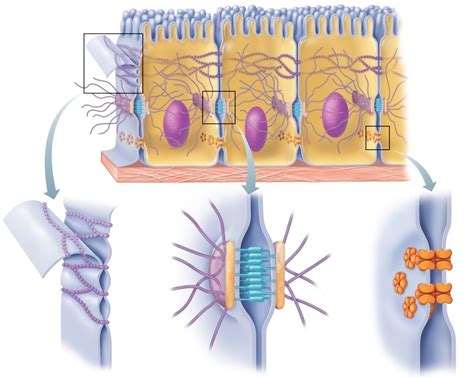
Types of Cell-Cell Junctions
There are several types of cell-cell junctions, including adherens junctions, tight junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions, and synaptic junctions. Each type of junction has distinct functions and characteristics, and they play important roles in maintaining tissue structure and regulating cell behavior. Adherens junctions, for example, are involved in cell adhesion and signaling, while tight junctions are involved in maintaining the barrier function of epithelial tissues. Desmosomes are involved in providing mechanical strength to tissues, while gap junctions are involved in cell-cell communication. Synaptic junctions, on the other hand, are involved in neurotransmission and are found in the nervous system.Adherens Junctions
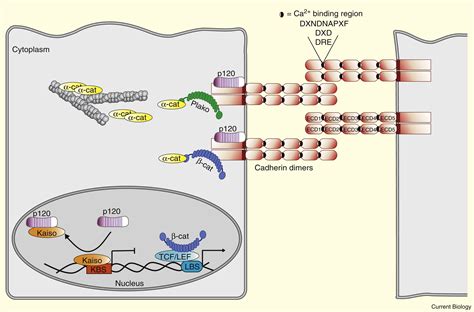
Functions of Adherens Junctions
Adherens junctions have several functions, including cell adhesion, signaling, and regulation of cell behavior. They are involved in the formation of tissue structure and the maintenance of tissue homeostasis. Adherens junctions are also involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival, and they play a crucial role in the development and maintenance of tissues.Tight Junctions
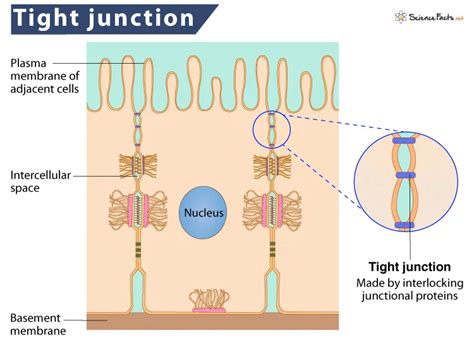
Functions of Tight Junctions
Tight junctions have several functions, including the regulation of ion transport, the maintenance of tissue homeostasis, and the prevention of disease. They are involved in the formation of the blood-brain barrier and the maintenance of the intestinal barrier. Tight junctions are also involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival, and they play a crucial role in the development and maintenance of tissues.Desmosomes
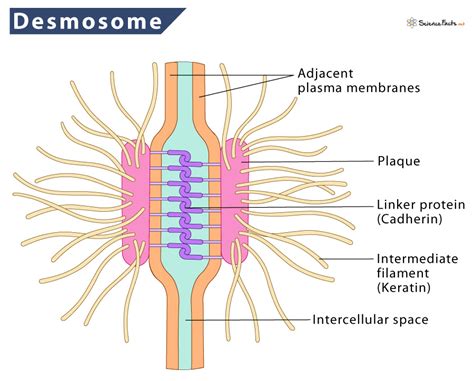
Functions of Desmosomes
Desmosomes have several functions, including the provision of mechanical strength to tissues and the regulation of cell behavior. They are involved in the maintenance of tissue structure and the prevention of disease. Desmosomes are also involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival, and they play a crucial role in the development and maintenance of tissues.Gap Junctions
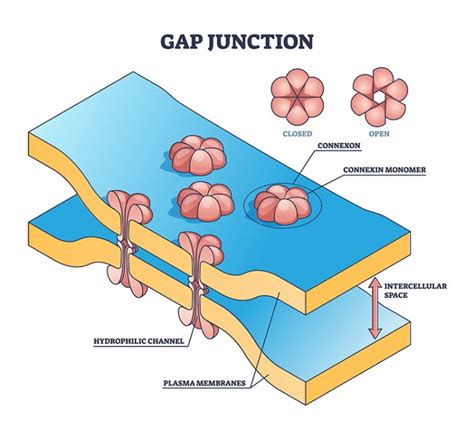
Functions of Gap Junctions
Gap junctions have several functions, including cell-cell communication, the regulation of cell behavior, and the coordination of tissue function. They are involved in the maintenance of tissue homeostasis and the prevention of disease. Gap junctions are also involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival, and they play a crucial role in the development and maintenance of tissues.Synaptic Junctions

Functions of Synaptic Junctions
Synaptic junctions have several functions, including neurotransmission, the regulation of cell behavior, and the coordination of tissue function. They are involved in the maintenance of tissue homeostasis and the prevention of disease. Synaptic junctions are also involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival, and they play a crucial role in the development and maintenance of tissues.Cell-Cell Junctions Image Gallery






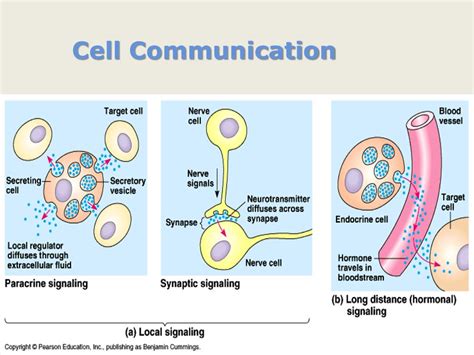
What are cell-cell junctions?
+Cell-cell junctions are specialized structures that form between adjacent cells and provide a physical link between them. These junctions play a crucial role in maintaining tissue structure, regulating cell behavior, and enabling cells to communicate with each other.
What are the different types of cell-cell junctions?
+There are several types of cell-cell junctions, including adherens junctions, tight junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions, and synaptic junctions. Each type of junction has distinct functions and characteristics, and they play important roles in maintaining tissue structure and regulating cell behavior.
What is the function of adherens junctions?
+Adherens junctions play a crucial role in cell adhesion and signaling. They are involved in the formation of tissue structure and the maintenance of tissue homeostasis. Adherens junctions are also involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival.
What is the function of tight junctions?
+Tight junctions play a crucial role in maintaining the barrier function of epithelial tissues. They are involved in the regulation of ion transport, the maintenance of tissue homeostasis, and the prevention of disease.
What is the function of desmosomes?
+Desmosomes play a crucial role in providing mechanical strength to tissues. They are involved in the maintenance of tissue structure and the regulation of cell behavior. Desmosomes are also involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival.
In conclusion, the 5 ways link cells, including adherens junctions, tight junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions, and synaptic junctions, play a crucial role in maintaining tissue structure, regulating cell behavior, and enabling cells to communicate with each other. Understanding how cells link together is essential for understanding various biological processes, including development, tissue repair, and disease. We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the different types of cell-cell junctions and their functions. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about this topic, please do not hesitate to comment or share this article with others.