Intro
Discover 5 ways Pareto chart analysis boosts quality control, defect identification, and process improvement, using statistical tools and problem-solving techniques.
The Pareto chart, also known as the Pareto analysis or Pareto diagram, is a statistical tool used to identify the most common problems or causes of problems in a process. It is named after Vilfredo Pareto, an Italian economist who first observed the principle that a small proportion of causes often leads to a large proportion of effects. In this article, we will explore 5 ways to use a Pareto chart to improve your business or organization.
The Pareto principle states that approximately 80% of problems are caused by 20% of the possible causes. This principle can be applied to various areas, such as quality control, inventory management, and customer service. By using a Pareto chart, you can visualize the data and identify the most significant problems or causes of problems, allowing you to focus your efforts on the most critical issues.
The importance of using a Pareto chart cannot be overstated. It helps you to prioritize your efforts, allocate resources more efficiently, and make data-driven decisions. In today's fast-paced business environment, it is essential to have a tool that can help you to quickly identify and solve problems, reducing waste and improving overall performance.
To entice readers to continue reading, let's consider a real-life example. Suppose you are a quality control manager in a manufacturing plant, and you are tasked with reducing the number of defective products. By using a Pareto chart, you can analyze the data and identify the most common causes of defects, such as machine errors or human mistakes. With this information, you can develop targeted strategies to address these issues, resulting in a significant reduction in defective products and improved customer satisfaction.
Introduction to Pareto Chart
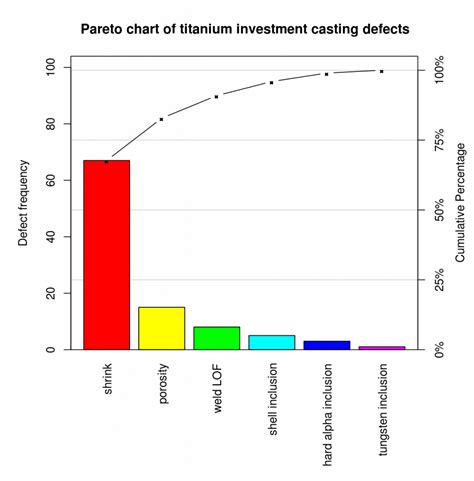
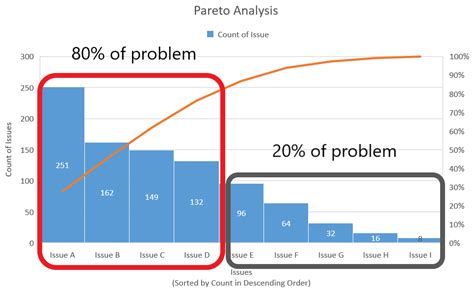
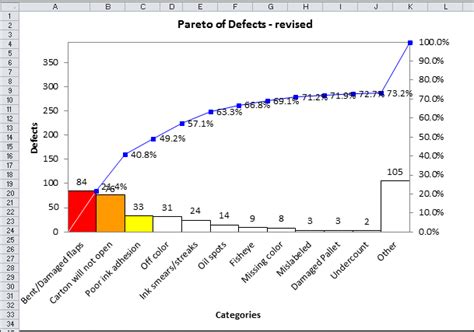
A Pareto chart is a type of bar chart that displays the relative frequency or size of items in a dataset. It is typically used to identify the most common problems or causes of problems in a process. The chart consists of two axes: the x-axis represents the categories or items, and the y-axis represents the frequency or size of each item. The bars are arranged in descending order, with the tallest bar on the left and the shortest bar on the right.
To create a Pareto chart, you need to collect data on the problems or causes of problems in your process. This can be done through surveys, observations, or analysis of existing data. Once you have collected the data, you can categorize it into different groups or items. Then, you can calculate the frequency or size of each item and create the Pareto chart.
Benefits of Using a Pareto Chart
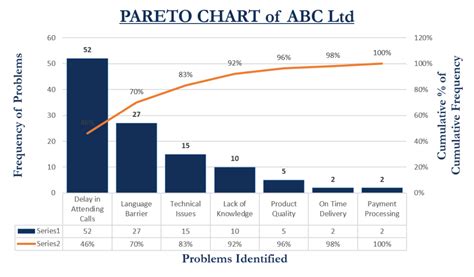
There are several benefits to using a Pareto chart. Firstly, it helps you to identify the most significant problems or causes of problems in your process. By focusing on the tallest bars on the left side of the chart, you can prioritize your efforts and allocate resources more efficiently. Secondly, it enables you to visualize the data and communicate the results to stakeholders more effectively. The chart provides a clear and concise picture of the problems or causes of problems, making it easier to understand and address them.
Thirdly, a Pareto chart helps you to develop targeted strategies to address the most critical issues. By analyzing the data and identifying the root causes of problems, you can develop effective solutions to mitigate or eliminate them. Finally, it allows you to monitor progress and evaluate the effectiveness of your strategies. By tracking changes in the Pareto chart over time, you can determine whether your efforts are yielding the desired results and make adjustments as needed.
How to Create a Pareto Chart
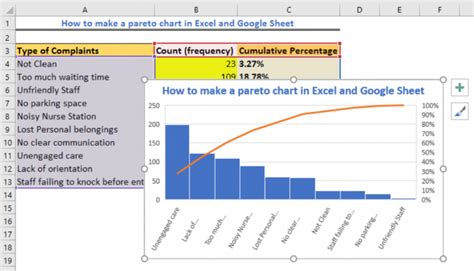
Creating a Pareto chart is a straightforward process that involves several steps. Firstly, you need to collect data on the problems or causes of problems in your process. This can be done through surveys, observations, or analysis of existing data. Secondly, you need to categorize the data into different groups or items. This can be done using categories such as machine errors, human mistakes, or material defects.
Thirdly, you need to calculate the frequency or size of each item. This can be done by counting the number of occurrences or measuring the size of each item. Fourthly, you need to create the Pareto chart using a bar chart or histogram. The x-axis should represent the categories or items, and the y-axis should represent the frequency or size of each item. Finally, you need to arrange the bars in descending order, with the tallest bar on the left and the shortest bar on the right.
5 Ways to Use a Pareto Chart
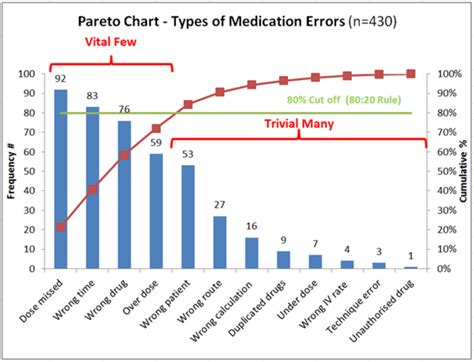
There are several ways to use a Pareto chart to improve your business or organization. Here are five examples:
- Quality Control: A Pareto chart can be used to identify the most common causes of defects in a manufacturing process. By analyzing the data and identifying the root causes of defects, you can develop targeted strategies to mitigate or eliminate them.
- Inventory Management: A Pareto chart can be used to identify the most commonly used items in an inventory. By focusing on the tallest bars on the left side of the chart, you can prioritize your inventory management efforts and ensure that the most critical items are always in stock.
- Customer Service: A Pareto chart can be used to identify the most common customer complaints or issues. By analyzing the data and identifying the root causes of customer dissatisfaction, you can develop targeted strategies to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Supply Chain Management: A Pareto chart can be used to identify the most critical suppliers or vendors in a supply chain. By focusing on the tallest bars on the left side of the chart, you can prioritize your supply chain management efforts and ensure that the most critical suppliers are always available.
- Process Improvement: A Pareto chart can be used to identify the most significant opportunities for process improvement. By analyzing the data and identifying the root causes of inefficiencies or waste, you can develop targeted strategies to improve process efficiency and reduce costs.
Best Practices for Using a Pareto Chart
There are several best practices to keep in mind when using a Pareto chart. Firstly, you should ensure that the data is accurate and reliable. This can be done by collecting data from multiple sources and verifying the results. Secondly, you should use a clear and concise title and labels on the chart. This will help to ensure that the chart is easy to understand and interpret.
Thirdly, you should use a logical and consistent categorization system. This will help to ensure that the data is organized in a way that makes sense and is easy to analyze. Fourthly, you should use a clear and concise scale on the y-axis. This will help to ensure that the chart is easy to read and understand. Finally, you should regularly review and update the chart to ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using a Pareto Chart
There are several common mistakes to avoid when using a Pareto chart. Firstly, you should avoid using a Pareto chart to analyze data that is not normally distributed. This can lead to inaccurate or misleading results. Secondly, you should avoid using a Pareto chart to analyze data that is too complex or has too many variables. This can make it difficult to interpret the results and identify the most significant problems or causes of problems.
Thirdly, you should avoid using a Pareto chart to analyze data that is not relevant or up-to-date. This can lead to inaccurate or misleading results and may not reflect the current situation. Fourthly, you should avoid using a Pareto chart to analyze data that is not accurate or reliable. This can lead to inaccurate or misleading results and may not reflect the true situation. Finally, you should avoid using a Pareto chart without proper training or expertise. This can lead to inaccurate or misleading results and may not reflect the true situation.
Gallery of Pareto Chart Examples
Pareto Chart Image Gallery

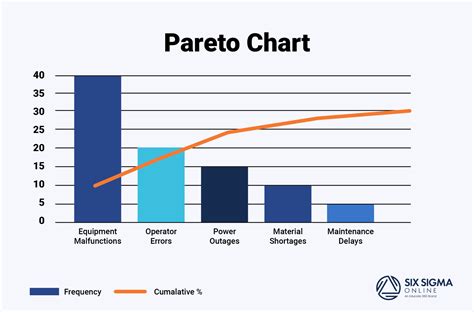
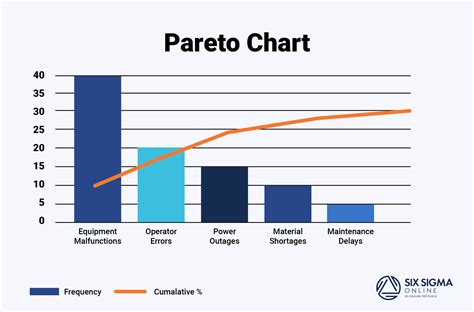
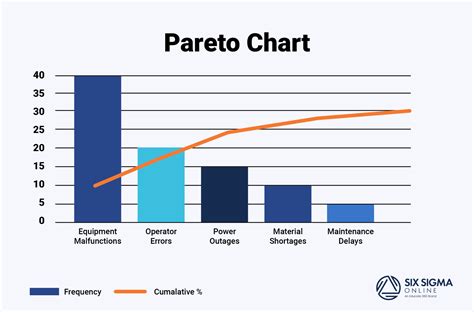
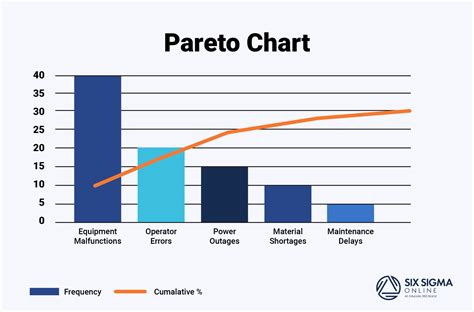
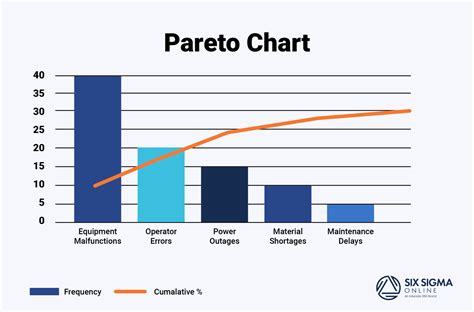
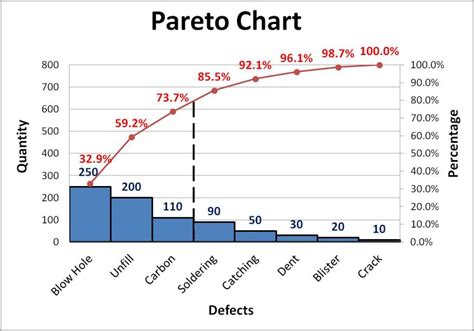
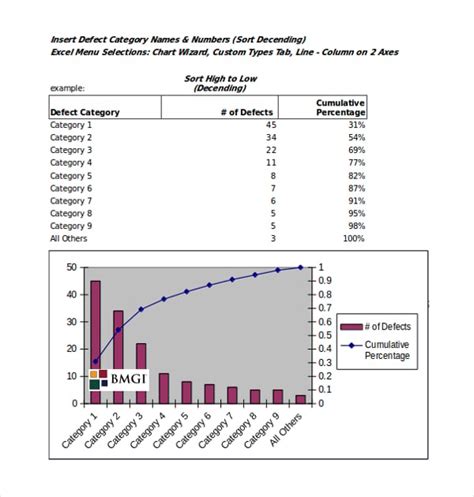
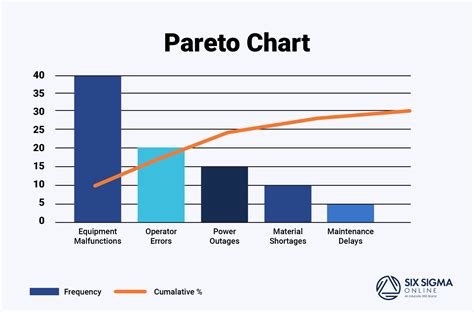
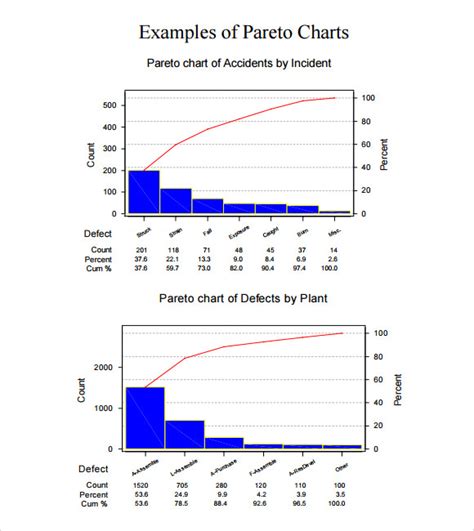
What is a Pareto chart?
+A Pareto chart is a type of bar chart that displays the relative frequency or size of items in a dataset. It is typically used to identify the most common problems or causes of problems in a process.
How do I create a Pareto chart?
+To create a Pareto chart, you need to collect data on the problems or causes of problems in your process. Then, you need to categorize the data into different groups or items, calculate the frequency or size of each item, and create the Pareto chart using a bar chart or histogram.
What are the benefits of using a Pareto chart?
+The benefits of using a Pareto chart include identifying the most significant problems or causes of problems, prioritizing efforts and allocating resources more efficiently, and developing targeted strategies to address the most critical issues.
In conclusion, a Pareto chart is a powerful tool that can help you to identify the most common problems or causes of problems in your process. By using a Pareto chart, you can prioritize your efforts, allocate resources more efficiently, and develop targeted strategies to address the most critical issues. We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the Pareto chart and its applications. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with using a Pareto chart, please feel free to comment below. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please share it with your colleagues and friends who may benefit from learning about the Pareto chart.