Intro
Learn Kruskal Wallis Test in Excel for non-parametric analysis, comparing multiple groups with ordinal data, using statistical software for hypothesis testing and data analysis.
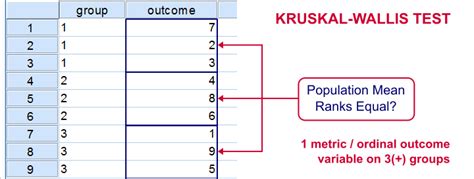
The Kruskal-Wallis test is a non-parametric statistical test used to compare more than two independent groups to determine if there are any statistically significant differences between them. It is an extension of the Wilcoxon rank-sum test and is used when the data does not meet the assumptions of parametric tests such as ANOVA. In this article, we will explore how to perform the Kruskal-Wallis test in Excel.
The Kruskal-Wallis test is a powerful tool for analyzing data that is not normally distributed or has unequal variances. It is commonly used in fields such as medicine, social sciences, and engineering, where data is often non-normal or has outliers. The test works by ranking the data and then comparing the mean ranks of each group to determine if there are any significant differences.
To perform the Kruskal-Wallis test in Excel, you will need to have the data analysis toolpack installed. This can be done by going to the "Data" tab and clicking on "Data Analysis" in the "Analysis" group. If you do not see the "Data Analysis" button, you may need to install the analysis toolpack by going to the "File" tab and clicking on "Options" and then "Add-ins".
Preparation of Data
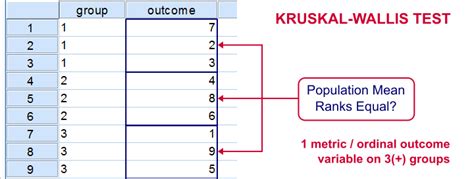
Before performing the Kruskal-Wallis test, it is essential to prepare the data. The data should be organized in a way that each group is in a separate column. The data should also be cleaned and checked for any missing or duplicate values.
Data Requirements
The Kruskal-Wallis test requires the following data: * At least three independent groups * Each group should have at least five observations * The data should be continuous or ordinal * The data should not be normally distributed or have unequal variancesPerforming the Kruskal-Wallis Test

To perform the Kruskal-Wallis test in Excel, follow these steps:
- Select the data range that includes all the groups
- Go to the "Data" tab and click on "Data Analysis" in the "Analysis" group
- Select "Kruskal-Wallis Test" from the list of available tests
- Click "OK" to run the test
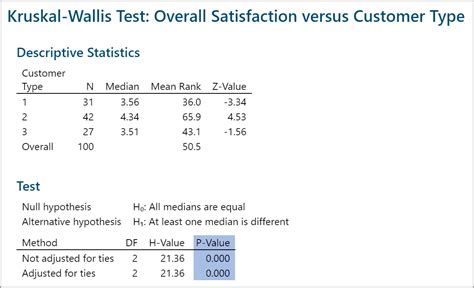
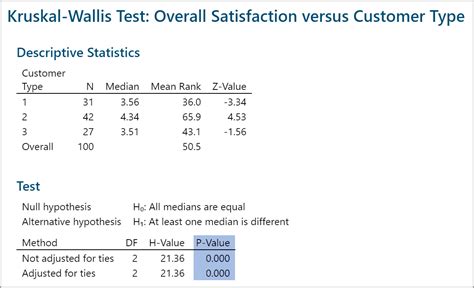
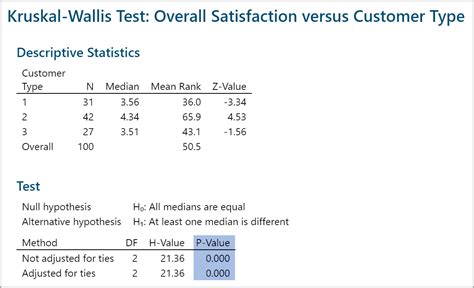
- The test will output the test statistic, degrees of freedom, and p-value
Interpreting the Results
The results of the Kruskal-Wallis test should be interpreted with caution. A low p-value (typically less than 0.05) indicates that there are statistically significant differences between the groups. However, the test does not indicate which groups are different from each other. To determine which groups are different, you will need to perform post-hoc tests such as the Dunn's test.Post-Hoc Tests

Post-hoc tests are used to determine which groups are different from each other after a significant Kruskal-Wallis test. The most common post-hoc test used with the Kruskal-Wallis test is the Dunn's test. The Dunn's test is a non-parametric test that compares each pair of groups to determine if there are any significant differences.
Dunn's Test
The Dunn's test is a pairwise comparison test that compares each pair of groups to determine if there are any significant differences. The test is performed by calculating the test statistic and p-value for each pair of groups. A low p-value (typically less than 0.05) indicates that there are statistically significant differences between the two groups.Example
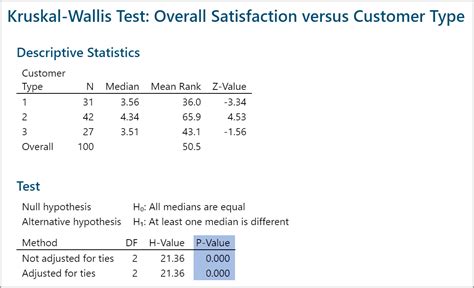
Suppose we want to compare the scores of three different groups of students. The data is as follows: Group 1: 10, 12, 15, 18, 20 Group 2: 8, 10, 12, 15, 18 Group 3: 12, 15, 18, 20, 22
To perform the Kruskal-Wallis test, we select the data range and go to the "Data" tab and click on "Data Analysis" in the "Analysis" group. We select "Kruskal-Wallis Test" from the list of available tests and click "OK" to run the test. The test outputs the test statistic, degrees of freedom, and p-value.
The p-value is less than 0.05, indicating that there are statistically significant differences between the groups. To determine which groups are different, we perform the Dunn's test. The Dunn's test outputs the test statistic and p-value for each pair of groups. The p-value for the comparison between Group 1 and Group 2 is less than 0.05, indicating that there are statistically significant differences between the two groups.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The Kruskal-Wallis test has several advantages, including:
- It is a non-parametric test, which means it does not require normality or equal variances
- It can handle ordinal data
- It is robust to outliers
However, the test also has some disadvantages, including:
- It assumes independence of observations
- It assumes that the data is continuous or ordinal
- It can be affected by tied values
Common Mistakes

There are several common mistakes that can be made when performing the Kruskal-Wallis test, including:
- Not checking for normality or equal variances before performing the test
- Not handling tied values correctly
- Not interpreting the results correctly
To avoid these mistakes, it is essential to carefully check the assumptions of the test and to interpret the results correctly.
Alternatives
There are several alternatives to the Kruskal-Wallis test, including:
- ANOVA: This is a parametric test that compares the means of three or more groups.
- Friedman test: This is a non-parametric test that compares the medians of three or more groups.
- Wilcoxon rank-sum test: This is a non-parametric test that compares the medians of two groups.
Each of these tests has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of test will depend on the specific research question and the characteristics of the data.
Kruskal Wallis Test Image Gallery




What is the Kruskal-Wallis test?
+The Kruskal-Wallis test is a non-parametric statistical test used to compare more than two independent groups to determine if there are any statistically significant differences between them.
What are the assumptions of the Kruskal-Wallis test?
+The Kruskal-Wallis test assumes independence of observations, continuity or ordinality of the data, and no tied values.
How do I perform the Kruskal-Wallis test in Excel?
+To perform the Kruskal-Wallis test in Excel, select the data range, go to the "Data" tab, and click on "Data Analysis" in the "Analysis" group. Select "Kruskal-Wallis Test" from the list of available tests and click "OK" to run the test.
How do I interpret the results of the Kruskal-Wallis test?
+The results of the Kruskal-Wallis test should be interpreted with caution. A low p-value (typically less than 0.05) indicates that there are statistically significant differences between the groups. However, the test does not indicate which groups are different from each other.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when performing the Kruskal-Wallis test?
+Some common mistakes to avoid when performing the Kruskal-Wallis test include not checking for normality or equal variances before performing the test, not handling tied values correctly, and not interpreting the results correctly.
In conclusion, the Kruskal-Wallis test is a powerful tool for analyzing data that is not normally distributed or has unequal variances. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can perform the Kruskal-Wallis test in Excel and interpret the results with confidence. Remember to check the assumptions of the test, handle tied values correctly, and interpret the results with caution. With practice and experience, you can become proficient in using the Kruskal-Wallis test to analyze your data and make informed decisions. We encourage you to share your experiences and ask questions in the comments section below.